Pain, affective symptoms, and cognitive deficits in patients with cerebral dopamine dysfunction
- PMID: 22386471
- PMCID: PMC3816524
- DOI: 10.1016/j.pain.2012.01.002
Pain, affective symptoms, and cognitive deficits in patients with cerebral dopamine dysfunction
Abstract
Converging preclinical, and human epidemiological, neuroimaging, and genetic evidence suggests a central role for dopamine neurotransmission in modulating pain perception and analgesia. Dysregulation in dopamine signaling may modulate the experience of pain both directly, by enhancing or diminishing the propagation of nociceptive signals, and indirectly, by influencing affective and cognitive processes, which affect the expectation, experience, and interpretation of nociceptive signals. Hypersensitivity to pain and high rates of comorbid chronic pain are common in disorders linked with deficits in dopamine system function, including disorders of mood and affect, substance abuse, and Parkinson disease. Hyposensitivity to pain, however, is common in patients with schizophrenia, which has been linked with excessive dopamine neurotransmission. Although patients are typically affected most by the primary symptoms of their disorders, alterations in pain perception may further increase the burden of their illness, compromising their quality of life. The present review focuses on this relationship, and discusses clinical and potential therapeutic implications for both patients with dopamine-related disorders and those with chronic pain syndromes.
Copyright © 2012 International Association for the Study of Pain. Published by Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures

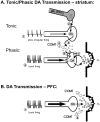
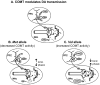
References
-
- Abercrombie ED, Keefe KA, DiFrischia DS, Zigmond MJ. Differential effect of stress on in vivo dopamine release in striatum, nucleus accumbens, and medial frontal cortex. J Neurochem. 1989;52:1655–1658. - PubMed
-
- Andersen PH, Gingrich JA, Bates MD, Dearry A, Falardeau P, Senogles SE, Caron MG. Dopamine receptor subtypes: beyond the D1/D2 classification. Trends Pharmacol Sci. 1990;11:231–236. - PubMed
-
- Apkarian AV, Bushnell MC, Treede RD, Zubieta JK. Human brain mechanisms of pain perception and regulation in health and disease. Eur J Pain. 2005;9:463–484. - PubMed
-
- Apkarian AV, Sosa Y, Krauss BR, Thomas PS, Fredrickson BE, Levy RE, Harden RN, Chialvo DR. Chronic pain patients are impaired on an emotional decision-making task. Pain. 2004;108:129–136. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

