Photochemical mechanisms of light-triggered release from nanocarriers
- PMID: 22386560
- PMCID: PMC3395781
- DOI: 10.1016/j.addr.2012.02.006
Photochemical mechanisms of light-triggered release from nanocarriers
Abstract
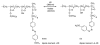
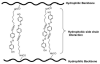
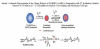
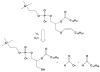
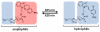
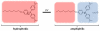
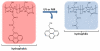
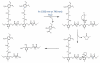
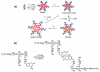
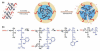
Over the last three decades, a handful of photochemical mechanisms have been applied to a large number of nanoscale assemblies that encapsulate a payload to afford spatio-temporal and remote control over activity of the encapsulated payload. Many of these systems are designed with an eye towards biomedical applications, as spatio-temporal and remote control of bioactivity would advance research and clinical practice. This review covers five underlying photochemical mechanisms that govern the activity of the majority of photoresponsive nanocarriers: 1. photo driven isomerization and oxidation, 2. surface plasmon absorption and photothermal effects, 3. photo driven hydrophobicity changes, 4. photo driven polymer backbone fragmentation and 5. photo driven de-crosslinking. The ways in which these mechanisms have been incorporated into nanocarriers and how they affect release are detailed, as well as the advantages and disadvantages of each system.
Copyright © 2012 Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
Figures
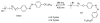
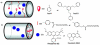


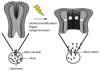


Similar articles
-
Photoresponsive hydrogels for biomedical applications.Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 2011 Nov;63(14-15):1257-66. doi: 10.1016/j.addr.2011.06.009. Epub 2011 Jul 2. Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 2011. PMID: 21745509 Review.
-
Smart Nanostructures for Cargo Delivery: Uncaging and Activating by Light.J Am Chem Soc. 2017 Apr 5;139(13):4584-4610. doi: 10.1021/jacs.6b08313. Epub 2017 Mar 13. J Am Chem Soc. 2017. PMID: 28192672 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Photo-responsive polymeric nanocarriers for target-specific and controlled drug delivery.Soft Matter. 2021 Oct 6;17(38):8577-8584. doi: 10.1039/d1sm00999k. Soft Matter. 2021. PMID: 34580698 Review.
-
Recent advances in near-infrared light-responsive nanocarriers for cancer therapy.Drug Discov Today. 2018 May;23(5):1115-1125. doi: 10.1016/j.drudis.2018.02.005. Epub 2018 Feb 23. Drug Discov Today. 2018. PMID: 29481876 Review.
-
Photoresponsive crosslinked hyperbranched polyglycerols as smart nanocarriers for guest binding and controlled release.Small. 2009 Oct;5(19):2199-204. doi: 10.1002/smll.200900465. Small. 2009. PMID: 19572327
Cited by
-
Remotely triggered cisplatin release from carbon nanocapsules by radiofrequency fields.Biomaterials. 2013 Feb;34(7):1862-9. doi: 10.1016/j.biomaterials.2012.11.033. Epub 2012 Dec 8. Biomaterials. 2013. PMID: 23228421 Free PMC article.
-
Multifunctional near-infrared light-triggered biodegradable micelles for chemo- and photo-thermal combination therapy.Oncotarget. 2016 Dec 13;7(50):82170-82184. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.10320. Oncotarget. 2016. PMID: 27366951 Free PMC article.
-
Light-Responsive and Dual-Targeting Liposomes: From Mechanisms to Targeting Strategies.Molecules. 2024 Jan 30;29(3):636. doi: 10.3390/molecules29030636. Molecules. 2024. PMID: 38338380 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Simultaneous delivery of Paclitaxel and Bcl-2 siRNA via pH-Sensitive liposomal nanocarrier for the synergistic treatment of melanoma.Sci Rep. 2016 Oct 27;6:35223. doi: 10.1038/srep35223. Sci Rep. 2016. PMID: 27786239 Free PMC article.
-
Photo-Induced Drug Release from Polymeric Micelles and Liposomes: Phototriggering Mechanisms in Drug Delivery Systems.Polymers (Basel). 2022 Mar 23;14(7):1286. doi: 10.3390/polym14071286. Polymers (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35406160 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Weissleder R. A clearer vision for in vivo imaging. Nat. Biotechnol. 2001;19:316–317. - PubMed
-
- Shum P, Kim J-M, Thompson DH. Phototriggering of liposomal drug delivery systems. Adv. Drug Del. Rev. 2001;53:273–284. - PubMed
-
- Alvarez-Lorenzo C, Bromberg L, Concheiro A. Light-sensitive intelligent drug delivery systems. Photochem. Photobiol. 2009;85:848–860. - PubMed
-
- Zhao Y. Photocontrollable block copolymer micelles: what can we control? J. Mater. Chem. 2009;19:4887–4895.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

