MicroRNAs regulate and provide robustness to the myogenic transcriptional network
- PMID: 22386695
- PMCID: PMC3369106
- DOI: 10.1016/j.coph.2012.02.001
MicroRNAs regulate and provide robustness to the myogenic transcriptional network
Abstract
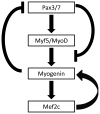
The genetics of skeletal muscle lineage commitment are deceptively complicated. MyoD overexpression is sufficient to convert fibroblasts into skeletal muscle myotubes. In vivo, there are a number of different steps of differentiation that require a large network of transcription factors that control differentiation and homeostasis of skeletal muscle progenitors. Each transcription factor has been shown to have the ability to promote the next factor in the cascade, but the mechanisms regulating the transitions remain incomplete. Recently, microRNAs have been shown to be important for a large number of developmental and oncogenic processes. In this review, we will discuss recent advances in the understanding of how microRNA is critical for skeletal muscle development by interacting with protein-coding genes that had previously been shown to be important for myogenesis.
Copyright © 2012 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Molecular and cellular regulation of skeletal myogenesis.Curr Top Dev Biol. 2014;110:1-73. doi: 10.1016/B978-0-12-405943-6.00001-4. Curr Top Dev Biol. 2014. PMID: 25248473 Review.
-
Muscle stem cells in developmental and regenerative myogenesis.Curr Opin Clin Nutr Metab Care. 2010 May;13(3):243-8. doi: 10.1097/MCO.0b013e328336ea98. Curr Opin Clin Nutr Metab Care. 2010. PMID: 20098319 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Comparative expression analysis of Pax3 and Pax7 during mouse myogenesis.Int J Dev Biol. 2006;50(1):47-54. doi: 10.1387/ijdb.052111dh. Int J Dev Biol. 2006. PMID: 16323077
-
Transcriptome analyses based on genetic screens for Pax3 myogenic targets in the mouse embryo.BMC Genomics. 2010 Dec 8;11:696. doi: 10.1186/1471-2164-11-696. BMC Genomics. 2010. PMID: 21143873 Free PMC article.
-
Pitx2c modulates Pax3+/Pax7+ cell populations and regulates Pax3 expression by repressing miR27 expression during myogenesis.Dev Biol. 2011 Sep 1;357(1):165-78. doi: 10.1016/j.ydbio.2011.06.039. Epub 2011 Jul 1. Dev Biol. 2011. PMID: 21749861
Cited by
-
miR-26a is required for skeletal muscle differentiation and regeneration in mice.Genes Dev. 2012 Oct 1;26(19):2180-91. doi: 10.1101/gad.198085.112. Genes Dev. 2012. PMID: 23028144 Free PMC article.
-
Long non-coding RNAs as emerging regulators of differentiation, development, and disease.Transcription. 2014;5(4):e944014. doi: 10.4161/21541272.2014.944014. Epub 2014 Oct 30. Transcription. 2014. PMID: 25483404 Free PMC article. Review.
-
MicroRNA-30a regulates zebrafish myogenesis through targeting the transcription factor Six1.J Cell Sci. 2014 May 15;127(Pt 10):2291-301. doi: 10.1242/jcs.143677. Epub 2014 Mar 14. J Cell Sci. 2014. PMID: 24634509 Free PMC article.
-
MUNC, a long noncoding RNA that facilitates the function of MyoD in skeletal myogenesis.Mol Cell Biol. 2015 Feb;35(3):498-513. doi: 10.1128/MCB.01079-14. Epub 2014 Nov 17. Mol Cell Biol. 2015. PMID: 25403490 Free PMC article.
-
MicroRNA-499 expression distinctively correlates to target genes sox6 and rod1 profiles to resolve the skeletal muscle phenotype in Nile tilapia.PLoS One. 2015 Mar 20;10(3):e0119804. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0119804. eCollection 2015. PLoS One. 2015. PMID: 25793727 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Tapscott SJ, Davis RL, Thayer MJ, Cheng PF, Weintraub H, Lassar AB. MyoD1: a nuclear phosphoprotein requiring a Myc homology region to convert fibroblasts to myoblasts. Science. 1988;242:405–411. - PubMed
-
- Berkes CA, Tapscott SJ. MyoD and the transcriptional control of myogenesis. Semin Cell Dev Biol. 2005;16:585–595. - PubMed
-
- Seale P, Sabourin LA, Girgis-Gabardo A, Mansouri A, Gruss P, Rudnicki MA. Pax7 is required for the specification of myogenic satellite cells. Cell. 2000;102:777–786. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources