Seroreactivity to LGL leukemia-specific epitopes in aplastic anemia, myelodysplastic syndrome and paroxysmal nocturnal hemoglobinuria: results of a bone marrow failure consortium study
- PMID: 22386729
- PMCID: PMC3312981
- DOI: 10.1016/j.leukres.2012.02.001
Seroreactivity to LGL leukemia-specific epitopes in aplastic anemia, myelodysplastic syndrome and paroxysmal nocturnal hemoglobinuria: results of a bone marrow failure consortium study
Abstract
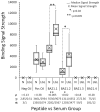
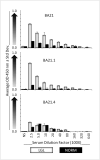
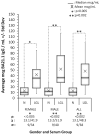
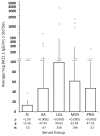
Large granular lymphocyte (LGL) leukemia is characterized by clonal expansion of antigen-activated cytotoxic T cells (CTL). Patients frequently exhibit seroreactivity against a human T-cell leukemia virus (HTLV) epitope, BA21. Aplastic anemia, paroxysmal nocturnal hemoglobinuria and myelodysplastic syndrome are bone marrow failure diseases that can also be associated with similar aberrant CTL activation (LGL-BMF). We identified a BA21 peptide that was specifically reactive with LGL leukemia sera and found significantly elevated antibody reactivity against the same peptide in LGL-BMF sera. This finding of shared seroreactivity in LGL-BMF conditions and LGL leukemia suggests that these diseases might share a common pathogenesis.
Copyright © 2012 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Figures
References
-
- Dearden C. Large granular lymphocytic leukaemia pathogenesis and management. Br J Haematol. 2011;152:273–83. - PubMed
-
- Melenhorst JJ, Sorbara L, Kirby M, et al. Large granular lymphocyte leukaemia is characterized by a clonal T-cell receptor rearrangement in both memory and effector CD8(+) lymphocyte populations. Br J Haematol. 2001;112:189–94. - PubMed
-
- Kothapalli R, Bailey RD, Kusmartseva I, et al. Constitutive expression of cytotoxic proteases and down-regulation of protease inhibitors in LGL leukemia. Int J Oncol. 2003;22:33–9. - PubMed
-
- Maciejewski JP, O’Keefe C, Gondek L, et al. Immune-mediated bone marrow failure syndromes of progenitor and stem cells: molecular analysis of cytotoxic T cell clones. Folia Histochem Cytobiol. 2007;45:5–14. - PubMed
-
- Plasilova M, Risitano A, Maciejewski JP. Application of the molecular analysis of the T-cell receptor repertoire in the study of immune-mediated hematologic diseases. Hematology. 2003;8:173–81. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

