R-loop formation is a distinctive characteristic of unmethylated human CpG island promoters
- PMID: 22387027
- PMCID: PMC3319272
- DOI: 10.1016/j.molcel.2012.01.017
R-loop formation is a distinctive characteristic of unmethylated human CpG island promoters
Abstract
CpG islands (CGIs) function as promoters for approximately 60% of human genes. Most of these elements remain protected from CpG methylation, a prevalent epigenetic modification associated with transcriptional silencing. Here, we report that methylation-resistant CGI promoters are characterized by significant strand asymmetry in the distribution of guanines and cytosines (GC skew) immediately downstream from their transcription start sites. Using innovative genomics methodologies, we show that transcription through regions of GC skew leads to the formation of long R loop structures. Furthermore, we show that GC skew and R loop formation potential is correlated with and predictive of the unmethylated state of CGIs. Finally, we provide evidence that R loop formation protects from DNMT3B1, the primary de novo DNA methyltransferase in early development. Altogether, these results suggest that protection from DNA methylation is a built-in characteristic of the DNA sequence of CGI promoters that is revealed by the cotranscriptional formation of R loop structures.
Copyright © 2012 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures
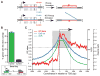


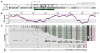



Comment in
-
R loops: lassoing DNA methylation at CpGi.Mol Cell. 2012 Mar 30;45(6):708-9. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2012.03.014. Mol Cell. 2012. PMID: 22464440
References
-
- Aguilera A, Gomez-Gonzalez B. Genome instability: a mechanistic view of its causes and consequences. Nat Rev Genet. 2008;9:204–217. - PubMed
-
- Bachman KE, Park BH, Rhee I, Rajagopalan H, Herman JG, Baylin SB, Kinzler KW, Vogelstein B. Histone modifications and silencing prior to DNA methylation of a tumor suppressor gene. Cancer Cell. 2003;3:89–95. - PubMed
-
- Barski A, Cuddapah S, Cui K, Roh TY, Schones DE, Wang Z, Wei G, Chepelev I, Zhao K. High-resolution profiling of histone methylations in the human genome. Cell. 2007;129:823–837. - PubMed
-
- Bird A. DNA methylation patterns and epigenetic memory. Genes Dev. 2002;16:6–21. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

