Chronic intermittent ethanol and withdrawal differentially modulate basolateral amygdala AMPA-type glutamate receptor function and trafficking
- PMID: 22387532
- PMCID: PMC3314101
- DOI: 10.1016/j.neuropharm.2012.02.017
Chronic intermittent ethanol and withdrawal differentially modulate basolateral amygdala AMPA-type glutamate receptor function and trafficking
Abstract
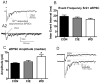
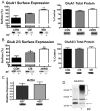
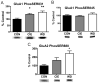
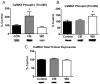
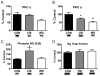
The amygdala plays a critical role in the generation and expression of anxiety-like behaviors including those expressed following withdrawal (WD) from chronic intermittent ethanol (CIE) exposure. In particular, the BLA glutamatergic system controls the expression of both innate and pathological anxiety. Recent data suggests that CIE and WD may functionally alter this system in a manner that closely parallels memory-related phenomena like long-term potentiation (LTP). We therefore specifically dissected CIE/WD-induced changes in glutamatergic signaling using electrophysiological and biochemical approaches with a particular focus on the plasticity-related components of this neurotransmitter system. Our results indicate that cortical glutamatergic inputs arriving at BLA principal via the external capsule undergo predominantly post-synaptic alterations in AMPA receptor function following CIE and WD. Biochemical analysis revealed treatment-dependent changes in AMPA receptor surface expression and subunit phosphorylation that are complemented by changes in total protein levels and/or phosphorylation status of several key, plasticity-associated protein kinases such as calcium/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase II (CaMKII) and protein kinase C (PKC). Together, these data show that CIE- and WD-induced changes in BLA glutamatergic function both functionally and biochemically mimic plasticity-related states. These mechanisms likely contribute to long-term increases in anxiety-like behavior following chronic ethanol exposure.
Copyright © 2012 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
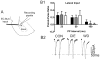
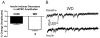
References
-
- Ahn SM, Choe ES. Alterations in GluR2 AMPA receptor phosphorylation at serine 880 following group I metabotropic glutamate receptor stimulation in the rat dorsal striatum. J Neurosci Res. 2009;88:992–999. - PubMed
-
- Andreasen M, Hablitz JJ. Paired-pulse facilitation in the dentate gyrus: a patch-clamp study in rat hippocampus in vitro. J Neurophysiol. 1994;72:326–336. - PubMed
-
- Appleby VJ, Corrêa SAL, Duckworth JK, Nash JE, Noël J, Fitzjohn SM, Collingridge GL, Molnár E. LTP in hippocampal neurons is associated with a CaMKII-mediated increase in GluA1 surface expression. J Neurochem. 2011;116:530–543. - PubMed
-
- Barria A, Muller D, Derkach V, Griffith LC, Soderling TR. Regulatory phosphorylation of AMPA-type glutamate receptors by CaM-KII during long-term potentiation. Science. 1997;276:2042–2045. - PubMed
-
- Beattie EC, Carroll RC, Yu X, Morishita W, Yasuda H, von Zastrow M, Malenka RC. Regulation of AMPA receptor endocytosis by a signaling mechanism shared with LTD. Nat Neurosci. 2000;3:1291–1300. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

