Metabolomics reveals the metabolic map of procainamide in humans and mice
- PMID: 22387617
- PMCID: PMC3665348
- DOI: 10.1016/j.bcp.2012.02.013
Metabolomics reveals the metabolic map of procainamide in humans and mice
Abstract
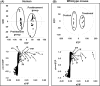
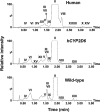
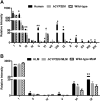
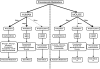
Procainamide, a type I antiarrhythmic agent, is used to treat a variety of atrial and ventricular dysrhythmias. It was reported that long-term therapy with procainamide may cause lupus erythematosus in 25-30% of patients. Interestingly, procainamide does not induce lupus erythematosus in mouse models. To explore the differences in this side-effect of procainamide between humans and mouse models, metabolomic analysis using ultra-performance liquid chromatography coupled with electrospray ionization quadrupole time-of-flight mass spectrometry (UPLC-ESI-QTOFMS) was conducted on urine samples from procainamide-treated humans, CYP2D6-humanized mice, and wild-type mice. Thirteen urinary procainamide metabolites, including nine novel metabolites, derived from P450-dependent, FMO-dependent oxidations and acylation reactions, were identified and structurally elucidated. In vivo metabolism of procainamide in CYP2D6-humanized mice as well as in vitro incubations with microsomes and recombinant P450s suggested that human CYP2D6 plays a major role in procainamide metabolism. Significant differences in N-acylation and N-oxidation of the drug between humans and mice largely account for the interspecies differences in procainamide metabolism. Significant levels of the novel N-oxide metabolites produced by FMO1 and FMO3 in humans might be associated with the development of procainamide-induced systemic lupus erythematosus. Observations based on this metabolomic study offer clues to understanding procainamide-induced lupus in humans and the effect of P450s and FMOs on procainamide N-oxidation.
Copyright © 2012 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures
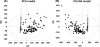




Similar articles
-
Involvement of CYP2D6 activity in the N-oxidation of procainamide in man.Pharmacogenetics. 1999 Dec;9(6):683-96. doi: 10.1097/01213011-199912000-00003. Pharmacogenetics. 1999. PMID: 10634131 Clinical Trial.
-
A comprehensive understanding of thioTEPA metabolism in the mouse using UPLC-ESI-QTOFMS-based metabolomics.Biochem Pharmacol. 2011 Apr 15;81(8):1043-53. doi: 10.1016/j.bcp.2011.01.024. Epub 2011 Feb 12. Biochem Pharmacol. 2011. PMID: 21300029 Free PMC article.
-
Metabolic profiling of dehydrodiisoeugenol using xenobiotic metabolomics.J Pharm Biomed Anal. 2017 Oct 25;145:725-733. doi: 10.1016/j.jpba.2017.07.045. Epub 2017 Jul 31. J Pharm Biomed Anal. 2017. PMID: 28806569
-
Metabolic map of osthole and its effect on lipids.Xenobiotica. 2018 Mar;48(3):285-299. doi: 10.1080/00498254.2017.1306660. Epub 2017 Apr 3. Xenobiotica. 2018. PMID: 28287022 Free PMC article.
-
Initiation of autoimmunity by a reactive metabolite of a lupus-inducing drug in the thymus.Environ Health Perspect. 1999 Oct;107 Suppl 5(Suppl 5):803-6. doi: 10.1289/ehp.99107s5803. Environ Health Perspect. 1999. PMID: 10502546 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Impaired clearance of sunitinib leads to metabolic disorders and hepatotoxicity.Br J Pharmacol. 2019 Jul;176(13):2162-2178. doi: 10.1111/bph.14664. Epub 2019 May 7. Br J Pharmacol. 2019. PMID: 30875096 Free PMC article.
-
Celastrol ameliorates acute liver injury through modulation of PPARα.Biochem Pharmacol. 2020 Aug;178:114058. doi: 10.1016/j.bcp.2020.114058. Epub 2020 May 26. Biochem Pharmacol. 2020. PMID: 32470546 Free PMC article.
-
Towards polypharmacokinetics: pharmacokinetics of multicomponent drugs and herbal medicines using a metabolomics approach.Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2013;2013:819147. doi: 10.1155/2013/819147. Epub 2013 Mar 14. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2013. PMID: 23573155 Free PMC article.
-
A rough guide to metabolite identification using high resolution liquid chromatography mass spectrometry in metabolomic profiling in metazoans.Comput Struct Biotechnol J. 2013 Feb 15;4:e201301005. doi: 10.5936/csbj.201301005. eCollection 2013. Comput Struct Biotechnol J. 2013. PMID: 24688687 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Application of Metabolomics in the Study of Natural Products.Nat Prod Bioprospect. 2018 Aug;8(4):321-334. doi: 10.1007/s13659-018-0175-9. Epub 2018 Jun 29. Nat Prod Bioprospect. 2018. PMID: 29959744 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Ribeiro C, Longo A. Procainamide and disopyramide. Eur Heart J. 1987;8(Suppl. A):11–9. - PubMed
-
- Bigger JT, Heissenbuttel RH. The use of procainamide and lidocaine in the treatment of cardiac arrhythmias. Prog Cardiovasc Dis. 1969;11:515–34. - PubMed
-
- Koch-Weser J. Procainamide dosage schedules, plasma concentration, and clinical effects. JAMA. 1971;215:1454–60. - PubMed
-
- Koch-Weser J. Pharmacokinetic of procainamide in man. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1971;179:370–82. - PubMed
-
- Strong JM, Dutcher JS, Lee WK, Atkinson AJ., Jr Pharmacokinetics in man of the N-acetylated metabolite of procainamide. J Pharmacokinet Biopharm. 1975;3:223–35. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

