Circulating ghrelin and GLP-1 are not affected by habitual diet
- PMID: 22387702
- PMCID: PMC3348389
- DOI: 10.1016/j.regpep.2012.02.001
Circulating ghrelin and GLP-1 are not affected by habitual diet
Abstract
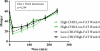
Background: Ghrelin and glucagon-like peptide-1 (GLP-1) are gut hormones known to induce hunger and satiety, respectively. Current knowledge about the effects of different macronutrients on circulating ghrelin and GLP-1 comes mainly from acute test meals, whereas little is known about the effects of chronic dietary intake on gut hormone secretion. This study was designed to examine whether 8-week habituation to diets with different percentages of carbohydrate and fat would affect serum ghrelin, GLP-1, and subjective hunger in a postabsorptive state and in response to a standard liquid mixed meal.
Methods: Sixty-one overweight men and women were provided all food for 8 weeks of either a higher-carbohydrate/lower-fat diet (High-CHO/Low-FAT; 55% CHO, 18% PRO, 27% FAT) or a lower-carbohydrate/higher-fat diet (Low-CHO/High-FAT; 43% CHO, 18% PRO, 39% FAT). After overnight fasts at baseline and week 8, participants consumed a standard liquid meal (7 kcals/kg, 58.6% CHO, 17.4% PRO, 24% FAT). Blood was sampled before the meal and at 15, 60, 90, 120, 180, and 240 min to determine total serum ghrelin and active GLP-1. Hunger was assessed by a visual analog scale. Mixed models were used to evaluate whether the temporal patterns of total serum ghrelin and active GLP-1 differed with diet.
Results: Although both diet groups reported greater hunger after 8 weeks (p=0.03), circulating ghrelin and GLP-1 were not affected by acclimation to different macronutrients.
Conclusion: Habituation to different diets does not appear to influence fasting ghrelin, fasting GLP-1, or responses of these gut hormones to a standard meal.
Copyright © 2012 Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
Figures


References
-
- Potier M, Darcel N, Tomé D. Protein, amino acids and the control of food intake. Curr Opin Clin Nutr Metab Care. 2009;12:54–8. - PubMed
-
- Ueno H, Shiiya T, Nakazato M. Translational research of ghrelin. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2010;1200:120–7. - PubMed
-
- Kojima M, Kangawa K. Ghrelin: more than endogenous growth hormone secretagogue. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2010;1200:140–8. - PubMed
-
- Cummings D, Purnell J, Frayo R, Schmidova K, Wisse B, Weigle D. A preprandial rise in plasma ghrelin levels suggests a role in meal initiation in humans. Diabetes. 2001;50:1714–9. - PubMed
-
- Bowen J, Noakes M, Trenerry C, Clifton PM. Energy intake, ghrelin, and cholecystokinin after different carbohydrate and protein preloads in overweight men. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2006;91:1477–83. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

