Mutations in axonemal dynein assembly factor DNAAF3 cause primary ciliary dyskinesia
- PMID: 22387996
- PMCID: PMC3315610
- DOI: 10.1038/ng.1106
Mutations in axonemal dynein assembly factor DNAAF3 cause primary ciliary dyskinesia
Abstract
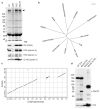
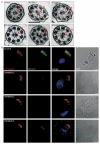
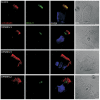
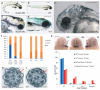
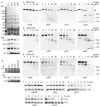
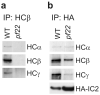
Primary ciliary dyskinesia most often arises from loss of the dynein motors that power ciliary beating. Here we show that DNAAF3 (also known as PF22), a previously uncharacterized protein, is essential for the preassembly of dyneins into complexes before their transport into cilia. We identified loss-of-function mutations in the human DNAAF3 gene in individuals from families with situs inversus and defects in the assembly of inner and outer dynein arms. Knockdown of dnaaf3 in zebrafish likewise disrupts dynein arm assembly and ciliary motility, causing primary ciliary dyskinesia phenotypes that include hydrocephalus and laterality malformations. Chlamydomonas reinhardtii PF22 is exclusively cytoplasmic, and a PF22-null mutant cannot assemble any outer and some inner dynein arms. Altered abundance of dynein subunits in mutant cytoplasm suggests that DNAAF3 (PF22) acts at a similar stage as other preassembly proteins, for example, DNAAF2 (also known as PF13 or KTU) and DNAAF1 (also known as ODA7 or LRRC50), in the dynein preassembly pathway. These results support the existence of a conserved, multistep pathway for the cytoplasmic formation of assembly competent ciliary dynein complexes.
Figures

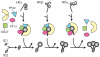
References
-
- Coren ME, Meeks M, Morrison I, Buchdahl RM, Bush A. Primary ciliary dyskinesia: age at diagnosis and symptom history. Acta Paediatr. 2002;91:667–669. - PubMed
-
- Bush A, Hogg C, Mitchison HM, Nisbet M, Wilson R. Update in primary ciliary dyskinesia. Clin. Pulm. Med. 2009;16:219–225.
-
- Bush A. Congenital heart disease in primary ciliary dyskinesia. Pediatr. Cardiol. 1998;19:191. - PubMed
-
- Kennedy MP, et al. Congenital heart disease and other heterotaxic defects in a large cohort of patients with primary ciliary dyskinesia. Circulation. 2007;115:2814–2821. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

