Prevention of β-amyloid degeneration of microglia by erythropoietin depends on Wnt1, the PI 3-K/mTOR pathway, Bad, and Bcl-xL
- PMID: 22388478
- PMCID: PMC3348479
- DOI: 10.18632/aging.100440
Prevention of β-amyloid degeneration of microglia by erythropoietin depends on Wnt1, the PI 3-K/mTOR pathway, Bad, and Bcl-xL
Abstract
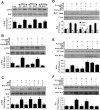
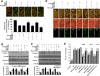
Central nervous system microglia promote neuronal regeneration and sequester toxic β-amyloid (Aβ) deposition during Alzheimer's disease. We show that the cytokine erythropoietin (EPO) decreases the toxic effect of Aβ on microgliain vitro. EPO up-regulates the cysteine-rich glycosylated wingless protein Wnt1 and activates the PI 3-K/Akt1/mTOR/ p70S6K pathway. This in turn increases phosphorylation and cytosol trafficking of Bad, reduces the Bad/Bcl-xL complex and increases the Bcl-xL/Bax complex, thus preventing caspase 1 and caspase 3 activation and apoptosis. Our data may foster development of novel strategies to use cytoprotectants such as EPO for Alzheimer's disease and other degenerative disorders.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors of this manuscript have no conflict of interest to declare.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Hyperoside protects primary rat cortical neurons from neurotoxicity induced by amyloid β-protein via the PI3K/Akt/Bad/Bcl(XL)-regulated mitochondrial apoptotic pathway.Eur J Pharmacol. 2011 Dec 15;672(1-3):45-55. doi: 10.1016/j.ejphar.2011.09.177. Epub 2011 Sep 29. Eur J Pharmacol. 2011. PMID: 21978835
-
Erythropoietin and Wnt1 govern pathways of mTOR, Apaf-1, and XIAP in inflammatory microglia.Curr Neurovasc Res. 2011 Nov;8(4):270-85. doi: 10.2174/156720211798120990. Curr Neurovasc Res. 2011. PMID: 22023617 Free PMC article.
-
ERK- and Akt-dependent neuroprotection by erythropoietin (EPO) against glyoxal-AGEs via modulation of Bcl-xL, Bax, and BAD.Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2010 Jan;51(1):35-46. doi: 10.1167/iovs.09-3544. Epub 2009 Jul 23. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2010. PMID: 19628748
-
Apoptosis in Alzheimer's disease: insight into the signaling pathways and therapeutic avenues.Apoptosis. 2023 Aug;28(7-8):943-957. doi: 10.1007/s10495-023-01848-y. Epub 2023 Apr 26. Apoptosis. 2023. PMID: 37186274 Review.
-
Erythropoietin: new directions for the nervous system.Int J Mol Sci. 2012;13(9):11102-11129. doi: 10.3390/ijms130911102. Epub 2012 Sep 6. Int J Mol Sci. 2012. PMID: 23109841 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Novel directions for diabetes mellitus drug discovery.Expert Opin Drug Discov. 2013 Jan;8(1):35-48. doi: 10.1517/17460441.2013.736485. Epub 2012 Oct 24. Expert Opin Drug Discov. 2013. PMID: 23092114 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Targeting the core of neurodegeneration: FoxO, mTOR, and SIRT1.Neural Regen Res. 2021 Mar;16(3):448-455. doi: 10.4103/1673-5374.291382. Neural Regen Res. 2021. PMID: 32985464 Free PMC article. Review.
-
NeuroEPO plus (NeuralCIM®) in mild-to-moderate Alzheimer's clinical syndrome: the ATHENEA randomized clinical trial.Alzheimers Res Ther. 2023 Dec 13;15(1):215. doi: 10.1186/s13195-023-01356-w. Alzheimers Res Ther. 2023. PMID: 38093366 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Erythropoietin as a Neuroprotective Molecule: An Overview of Its Therapeutic Potential in Neurodegenerative Diseases.ASN Neuro. 2019 Jan-Dec;11:1759091419871420. doi: 10.1177/1759091419871420. ASN Neuro. 2019. PMID: 31450955 Free PMC article. Review.
-
17β‑Estradiol protects against interleukin‑1β‑induced apoptosis in rat nucleus pulposus cells via the mTOR/caspase‑3 pathway.Mol Med Rep. 2019 Aug;20(2):1523-1530. doi: 10.3892/mmr.2019.10384. Epub 2019 Jun 13. Mol Med Rep. 2019. PMID: 31257459 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Erol A. Unraveling the Molecular Mechanisms Behind the Metabolic Basis of Sporadic Alzheimer's Disease. J Alzheimers Dis. 2009 - PubMed
-
- Salminen A, Kaarniranta K, Haapasalo A, Soininen H, Hiltunen M. AMP-activated protein kinase: a potential player in Alzheimer's disease. J Neurochem. 2011;118:460–474. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

