A GAIN in understanding autoproteolytic G protein-coupled receptors and polycystic kidney disease proteins
- PMID: 22388517
- PMCID: PMC3321188
- DOI: 10.1038/emboj.2012.51
A GAIN in understanding autoproteolytic G protein-coupled receptors and polycystic kidney disease proteins
Abstract
EMBO J 31 6, 1364–1378 (2012); published online January 14 2012
A large and poorly understood class of G protein-coupled receptors (GPCRs) are involved in cell adhesion and contain an autoproteolytic site known as the GPCR proteolysis site (GPS) located immediately N-terminal to the first transmembrane span. This motif of ∼50 amino acids is also found juxtaposed to the first transmembrane span of an unrelated family of proteins associated with polycystic kidney disease (PKD), but its structural and functional roles were not clear. In this issue of The EMBO Journal, Arac et al use X-ray crystallography to show that the GPS motif is merely the C-terminal end of a much larger
Conflict of interest statement
The author declares that he has no conflict of interest.
Figures
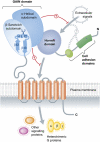
Comment on
-
A novel evolutionarily conserved domain of cell-adhesion GPCRs mediates autoproteolysis.EMBO J. 2012 Mar 21;31(6):1364-78. doi: 10.1038/emboj.2012.26. Epub 2012 Feb 14. EMBO J. 2012. PMID: 22333914 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Brannigan JA, Dodson G, Duggleby HJ, Moody PC, Smith JL, Tomchick DR, Murzin AG (1995) A protein catalytic framework with an N-terminal nucleophile is capable of self-activation. Nature 378: 416–419 - PubMed
-
- Ichtchenko K, Bittner MA, Krasnoperov V, Little AR, Chepurny O, Holz RW, Petrenko AG (1999) A novel ubiquitously expressed α-latrotoxin receptor is a member of the CIRL family of G-protein-coupled receptors. J Biol Chem 274: 5491–5498 - PubMed
-
- Krasnoperov V, Lu Y, Buryanovsky L, Neubert TA, Ichtchenko K, Petrenko AG (2002) Post-translational proteolytic processing of the calcium-independent receptor of α-latrotoxin (CIRL), a natural chimera of the cell adhesion protein and the G protein-coupled receptor. Role of the G protein-coupled receptor proteolysis site (GPS) motif. J Biol Chem 277: 46518–46526 - PubMed
-
- Lin HH, Chang GW, Davies JQ, Stacey M, Harris J, Gordon S (2004) Autocatalytic cleavage of the EMR2 receptor occurs at a conserved G protein-coupled receptor proteolytic site motif. J Biol Chem 279: 31823–31832 - PubMed

