Metabolic engineering of Saccharomyces cerevisiae: a key cell factory platform for future biorefineries
- PMID: 22388689
- PMCID: PMC11115109
- DOI: 10.1007/s00018-012-0945-1
Metabolic engineering of Saccharomyces cerevisiae: a key cell factory platform for future biorefineries
Abstract
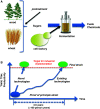
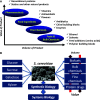
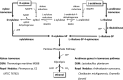
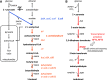
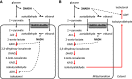
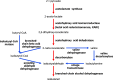
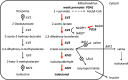
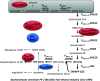
Metabolic engineering is the enabling science of development of efficient cell factories for the production of fuels, chemicals, pharmaceuticals, and food ingredients through microbial fermentations. The yeast Saccharomyces cerevisiae is a key cell factory already used for the production of a wide range of industrial products, and here we review ongoing work, particularly in industry, on using this organism for the production of butanol, which can be used as biofuel, and isoprenoids, which can find a wide range of applications including as pharmaceuticals and as biodiesel. We also look into how engineering of yeast can lead to improved uptake of sugars that are present in biomass hydrolyzates, and hereby allow for utilization of biomass as feedstock in the production of fuels and chemicals employing S. cerevisiae. Finally, we discuss the perspectives of how technologies from systems biology and synthetic biology can be used to advance metabolic engineering of yeast.
Figures

References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

