The specific targeting of immune regulation: T-cell responses against Indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase
- PMID: 22388712
- PMCID: PMC3401509
- DOI: 10.1007/s00262-012-1234-4
The specific targeting of immune regulation: T-cell responses against Indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase
Abstract
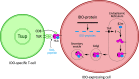
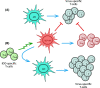
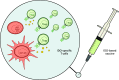
Indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase (IDO) is an immunoregulatory enzyme that is implicated in suppressing T-cell immunity in many settings including cancer. In recent years, we have described spontaneous CD8(+) as well as CD4(+) T-cell reactivity against IDO in the tumor microenvironment of different cancer patients as well as in the peripheral blood of both cancer patients and to a lesser extent in healthy donors. We have demonstrated that IDO-reactive CD8(+) T cells were peptide-specific, cytotoxic effector cells, which are able to recognize and kill IDO-expressing cells including tumor cells as well as dendritic cells. Consequently, IDO may serve as a widely applicable target for immunotherapeutic strategies with a completely different function as well as expression pattern compared to previously described antigens. IDO constitutes a significant counter-regulatory mechanism induced by pro-inflammatory signals, and IDO-based immunotherapy may consequently be synergistic with additional immunotherapy. In this regard, we have shown that the presence of IDO-specific T cells boosted immunity against CMV and tumor antigens by eliminating IDO(+) suppressive cells and changing the regulatory microenvironment. The current review summarizes current knowledge of IDO as a T-cell antigen, reports the initial results that are suggesting a general function of IDO-specific T cells in immunoregulation, and discusses future opportunities.
Trial registration: ClinicalTrials.gov NCT01219348.
Conflict of interest statement
The author has previously filed a patent application based on the use of IDO for vaccination. The rights of the patent application have been transferred to Herlev Hospital through the Capital Region of Denmark.
Figures
Similar articles
-
The immune system strikes back: cellular immune responses against indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase.PLoS One. 2009 Sep 7;4(9):e6910. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0006910. PLoS One. 2009. PMID: 19738905 Free PMC article.
-
Indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase specific, cytotoxic T cells as immune regulators.Blood. 2011 Feb 17;117(7):2200-10. doi: 10.1182/blood-2010-06-288498. Epub 2010 Nov 15. Blood. 2011. PMID: 21079151 Free PMC article.
-
Natural CD4+ T-cell responses against indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase.PLoS One. 2012;7(4):e34568. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0034568. Epub 2012 Apr 23. PLoS One. 2012. PMID: 22539948 Free PMC article.
-
Indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase in T-cell tolerance and tumoral immune escape.Immunol Rev. 2008 Apr;222:206-21. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-065X.2008.00610.x. Immunol Rev. 2008. PMID: 18364004 Review.
-
IDO in the Tumor Microenvironment: Inflammation, Counter-Regulation, and Tolerance.Trends Immunol. 2016 Mar;37(3):193-207. doi: 10.1016/j.it.2016.01.002. Epub 2016 Jan 31. Trends Immunol. 2016. PMID: 26839260 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
The immunosuppressive role of indoleamine 2, 3-dioxygenase in glioblastoma: mechanism of action and immunotherapeutic strategies.Med Oncol. 2022 Jun 18;39(9):130. doi: 10.1007/s12032-022-01724-w. Med Oncol. 2022. PMID: 35716323 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Interstitial Foci Expression of Indoleamine 2,3-Dioxygenase 1: A Potential Biomarker for Kidney Transplant Rejection.J Clin Med. 2024 Jul 22;13(14):4265. doi: 10.3390/jcm13144265. J Clin Med. 2024. PMID: 39064305 Free PMC article.
-
Indoleamine 2,3-Dioxygenase 1 (IDO1) in Kidney Transplantation: A Guardian against Rejection.J Clin Med. 2023 Dec 6;12(24):7531. doi: 10.3390/jcm12247531. J Clin Med. 2023. PMID: 38137602 Free PMC article.
-
Immune-suppressive properties of the tumor microenvironment.Cancer Immunol Immunother. 2013 Jul;62(7):1137-48. doi: 10.1007/s00262-013-1434-6. Epub 2013 May 11. Cancer Immunol Immunother. 2013. PMID: 23666510 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase (IDO) is frequently expressed in stromal cells of Hodgkin lymphoma and is associated with adverse clinical features: a retrospective cohort study.BMC Cancer. 2014 May 15;14:335. doi: 10.1186/1471-2407-14-335. BMC Cancer. 2014. PMID: 24886161 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Baban B, Hansen AM, Chandler PR, Manlapat A, Bingaman A, Kahler DJ, Munn DH, Mellor AL. A minor population of splenic dendritic cells expressing CD19 mediates IDO-dependent T cell suppression via type I IFN signaling following B7 ligation. Int Immunol. 2005;17(7):909–919. doi: 10.1093/intimm/dxh271. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Bauer TM, Jiga LP, Chuang JJ, Randazzo M, Opelz G, Terness P. Studying the immunosuppressive role of indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase: tryptophan metabolites suppress rat allogeneic T-cell responses in vitro and in vivo. Transpl Int. 2005;18(1):95–100. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-2277.2004.00031.x. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

