The specific targeting of immune regulation: T-cell responses against Indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase
- PMID: 22388712
- PMCID: PMC3401509
- DOI: 10.1007/s00262-012-1234-4
The specific targeting of immune regulation: T-cell responses against Indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase
Abstract
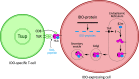
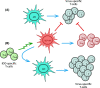
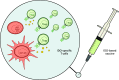
Indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase (IDO) is an immunoregulatory enzyme that is implicated in suppressing T-cell immunity in many settings including cancer. In recent years, we have described spontaneous CD8(+) as well as CD4(+) T-cell reactivity against IDO in the tumor microenvironment of different cancer patients as well as in the peripheral blood of both cancer patients and to a lesser extent in healthy donors. We have demonstrated that IDO-reactive CD8(+) T cells were peptide-specific, cytotoxic effector cells, which are able to recognize and kill IDO-expressing cells including tumor cells as well as dendritic cells. Consequently, IDO may serve as a widely applicable target for immunotherapeutic strategies with a completely different function as well as expression pattern compared to previously described antigens. IDO constitutes a significant counter-regulatory mechanism induced by pro-inflammatory signals, and IDO-based immunotherapy may consequently be synergistic with additional immunotherapy. In this regard, we have shown that the presence of IDO-specific T cells boosted immunity against CMV and tumor antigens by eliminating IDO(+) suppressive cells and changing the regulatory microenvironment. The current review summarizes current knowledge of IDO as a T-cell antigen, reports the initial results that are suggesting a general function of IDO-specific T cells in immunoregulation, and discusses future opportunities.
Trial registration: ClinicalTrials.gov NCT01219348.
Conflict of interest statement
The author has previously filed a patent application based on the use of IDO for vaccination. The rights of the patent application have been transferred to Herlev Hospital through the Capital Region of Denmark.
Figures
References
-
- Baban B, Hansen AM, Chandler PR, Manlapat A, Bingaman A, Kahler DJ, Munn DH, Mellor AL. A minor population of splenic dendritic cells expressing CD19 mediates IDO-dependent T cell suppression via type I IFN signaling following B7 ligation. Int Immunol. 2005;17(7):909–919. doi: 10.1093/intimm/dxh271. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Bauer TM, Jiga LP, Chuang JJ, Randazzo M, Opelz G, Terness P. Studying the immunosuppressive role of indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase: tryptophan metabolites suppress rat allogeneic T-cell responses in vitro and in vivo. Transpl Int. 2005;18(1):95–100. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-2277.2004.00031.x. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

