An epigenetic blockade of cognitive functions in the neurodegenerating brain
- PMID: 22388814
- PMCID: PMC3498952
- DOI: 10.1038/nature10849
An epigenetic blockade of cognitive functions in the neurodegenerating brain
Abstract
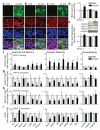
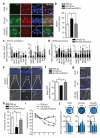
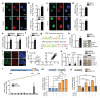
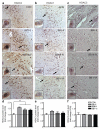
Cognitive decline is a debilitating feature of most neurodegenerative diseases of the central nervous system, including Alzheimer's disease. The causes leading to such impairment are only poorly understood and effective treatments are slow to emerge. Here we show that cognitive capacities in the neurodegenerating brain are constrained by an epigenetic blockade of gene transcription that is potentially reversible. This blockade is mediated by histone deacetylase 2, which is increased by Alzheimer's-disease-related neurotoxic insults in vitro, in two mouse models of neurodegeneration and in patients with Alzheimer's disease. Histone deacetylase 2 associates with and reduces the histone acetylation of genes important for learning and memory, which show a concomitant decrease in expression. Importantly, reversing the build-up of histone deacetylase 2 by short-hairpin-RNA-mediated knockdown unlocks the repression of these genes, reinstates structural and synaptic plasticity, and abolishes neurodegeneration-associated memory impairments. These findings advocate for the development of selective inhibitors of histone deacetylase 2 and suggest that cognitive capacities following neurodegeneration are not entirely lost, but merely impaired by this epigenetic blockade.
Figures
References
-
- Walsh DM, Selkoe DJ. Deciphering the molecular basis of memory failure in Alzheimer’s disease. Neuron. 2004;44:181–93. - PubMed
-
- Kandel ER. The molecular biology of memory storage: a dialogue between genes and synapses. Science. 2001;294:1030–8. - PubMed
-
- Gräff J, Kim D, Dobbin MM, Tsai LH. Epigenetic regulation of gene expression in physiological and pathological brain processes. Physiol Rev. 2011;91:603–49. - PubMed
-
- Brownell JE, Allis CD. Special HATs for special occasions: linking histone acetylation to chromatin assembly and gene activation. Curr Opin Genet Dev. 1996;6:176–84. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

