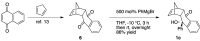Anti-addition mechanism in the intramolecular hydroalkoxylation of alkenes catalyzed by PVP-stabilized nanogold
- PMID: 22388968
- PMCID: PMC6268499
- DOI: 10.3390/molecules17032579
Anti-addition mechanism in the intramolecular hydroalkoxylation of alkenes catalyzed by PVP-stabilized nanogold
Abstract
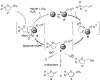
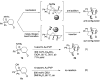
(1R*,4S*,4aR*,9aS*,10S*)-10-Hydroxy-10-phenyl-1,4a,9a,10-tetrahydro-1,4-methanoanthracen-9(4H)-one (1c) was prepared for the elucidation of the reaction mechanism of intramolecular hydroalkoxylation of alkenes catalyzed by gold nanoclusters stabilized by a hydrophilic polymer, poly(N-vinyl-2-pyrrolidone) (Au:PVP). It was found that the reaction proceeded via anti-addition of alcohol to the alkene assisted by p-activation of the gold clusters, which is the same mechanism as the hydroamination by toluenesulfonamides.
Figures
References
-
- Haruta M., Kobayashi T., Sano H., Yamada N. Novel gold catalysts for the oxidation of carbon monoxide at a temperature far below 0 °C. Chem. Lett. 1987:405–408.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources