Characterization of the response to zinc deficiency in the cyanobacterium Anabaena sp. strain PCC 7120
- PMID: 22389488
- PMCID: PMC3347182
- DOI: 10.1128/JB.00090-12
Characterization of the response to zinc deficiency in the cyanobacterium Anabaena sp. strain PCC 7120
Abstract
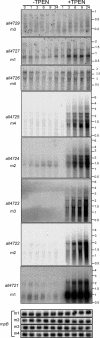
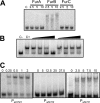
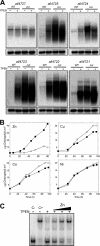
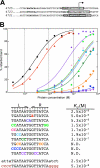
Zur regulators control zinc homeostasis by repressing target genes under zinc-sufficient conditions in a wide variety of bacteria. This paper describes how part of a survey of duplicated genes led to the identification of the open reading frame all2473 as the gene encoding the Zur regulator of the cyanobacterium Anabaena sp. strain PCC 7120. All2473 binds to DNA in a zinc-dependent manner, and its DNA-binding sequence was characterized, which allowed us to determine the relative contribution of particular nucleotides to Zur binding. A zur mutant was found to be impaired in the regulation of zinc homeostasis, showing sensitivity to elevated concentrations of zinc but not other metals. In an effort to characterize the Zur regulon in Anabaena, 23 genes containing upstream putative Zur-binding sequences were identified and found to be regulated by Zur. These genes are organized in six single transcriptional units and six operons, some of them containing multiple Zur-regulated promoters. The identities of genes of the Zur regulon indicate that Anabaena adapts to conditions of zinc deficiency by replacing zinc metalloproteins with paralogues that fulfill the same function but presumably with a lower zinc demand, and with inducing putative metallochaperones and membrane transport systems likely being involved in the scavenging of extracellular zinc, including plasma membrane ABC transport systems and outer membrane TonB-dependent receptors. Among the Zur-regulated genes, the ones showing the highest induction level encode proteins of the outer membrane, suggesting a primary role for components of this cell compartment in the capture of zinc cations from the extracellular medium.
Figures


Comment in
-
Zinc starvation response in a cyanobacterium revealed.J Bacteriol. 2012 May;194(10):2407-12. doi: 10.1128/JB.00257-12. Epub 2012 Mar 2. J Bacteriol. 2012. PMID: 22389477 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- Ausubel FM, et al. 2010. Current protocols in molecular biology. Greene Publishing & Wiley-Interscience, New York, NY
-
- Baichoo N, Wang T, Ye R, Helmann JD. 2002. Global analysis of the Bacillus subtilis Fur regulon and the iron starvation stimulon. Mol. Microbiol. 45:1613–1629 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

