Magnetite Nanoparticles for Medical MR Imaging
- PMID: 22389583
- PMCID: PMC3290401
- DOI: 10.1016/S1369-7021(11)70163-8
Magnetite Nanoparticles for Medical MR Imaging
Abstract
Nanotechnology has given scientists new tools for the development of advanced materials for the detection and diagnosis of disease. Iron oxide nanoparticles (SPIONs) in particular have been extensively investigated as novel magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) contrast agents due to a combination of favorable superparamagnetic properties, biodegradability, and surface properties of easy modification for improved in vivo kinetics and multifunctionality. This review discusses the basics of MR imaging, the origin of SPION's unique magnetic properties, recent developments in MRI acquisition methods for detection of SPIONs, synthesis and post-synthesis processes that improve SPION's imaging characteristics, and an outlook on the translational potential of SPIONs.
Figures

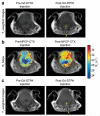


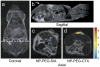
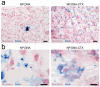

References
-
- Edelman RD, et al. MRI: Clinical Magnetic Resonance Imaging. 2 ed W. B. Saunders Company; Philadelphia, Pennsylvania: 1996. p. 1150.
-
- Ferrari M. Nat Rev Cancer. 2005;5(3):161. - PubMed
-
- Wickline SA, et al. Journal of Magnetic Resonance Imaging. 2007;25(4):667. - PubMed
-
- Corot C, et al. Invest. Radiol. 2004;39(10):619. - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
