Prenatal detection of aneuploidy and imbalanced chromosomal arrangements by massively parallel sequencing
- PMID: 22389664
- PMCID: PMC3289612
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0027835
Prenatal detection of aneuploidy and imbalanced chromosomal arrangements by massively parallel sequencing
Abstract
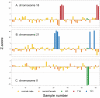
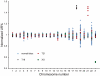
Fetal chromosomal abnormalities are the most common reasons for invasive prenatal testing. Currently, G-band karyotyping and several molecular genetic methods have been established for diagnosis of chromosomal abnormalities. Although these testing methods are highly reliable, the major limitation remains restricted resolutions or can only achieve limited coverage on the human genome at one time. The massively parallel sequencing (MPS) technologies which can reach single base pair resolution allows detection of genome-wide intragenic deletions and duplication challenging karyotyping and microarrays as the tool for prenatal diagnosis. Here we reported a novel and robust MPS-based method to detect aneuploidy and imbalanced chromosomal arrangements in amniotic fluid (AF) samples. We sequenced 62 AF samples on Illumina GAIIx platform and with averagely 0.01× whole genome sequencing data we detected 13 samples with numerical chromosomal abnormalities by z-test. With up to 2× whole genome sequencing data we were able to detect microdeletion/microduplication (ranged from 1.4 Mb to 37.3 Mb of 5 samples from chorionic villus sampling (CVS) using SeqSeq algorithm. Our work demonstrated MPS is a robust and accurate approach to detect aneuploidy and imbalanced chromosomal arrangements in prenatal samples.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
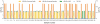
References
-
- Driscoll DA, Gross S. Clinical practice. Prenatal screening for aneuploidy. N Engl J Med. 2009;360:2556–2562. - PubMed
-
- Hook EB. Rates of chromosome abnormalities at different maternal ages. Obstet Gynecol. 1981;58:282–285. - PubMed
-
- Morris JK, Wald NJ, Mutton DE, Alberman E. Comparison of models of maternal age-specific risk for Down syndrome live births. Prenat Diagn. 2003;23:252–258. - PubMed
-
- Wapner RJ. Genetics of stillbirth. Clin Obstet Gynecol. 2010;53:628–634. - PubMed
-
- Korteweg FJ, Bouman K, Erwich JJ, Timmer A, Veeger NJ, et al. Cytogenetic analysis after evaluation of 750 fetal deaths: proposal for diagnostic workup. Obstet Gynecol. 2008;111:865–874. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

