Adipocyte-specific protein tyrosine phosphatase 1B deletion increases lipogenesis, adipocyte cell size and is a minor regulator of glucose homeostasis
- PMID: 22389718
- PMCID: PMC3289674
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0032700
Adipocyte-specific protein tyrosine phosphatase 1B deletion increases lipogenesis, adipocyte cell size and is a minor regulator of glucose homeostasis
Abstract
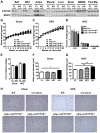
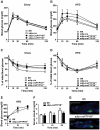
Protein tyrosine phosphatase 1B (PTP1B), a key negative regulator of leptin and insulin signaling, is positively correlated with adiposity and contributes to insulin resistance. Global PTP1B deletion improves diet-induced obesity and glucose homeostasis via enhanced leptin signaling in the brain and increased insulin signaling in liver and muscle. However, the role of PTP1B in adipocytes is unclear, with studies demonstrating beneficial, detrimental or no effect(s) of adipose-PTP1B-deficiency on body mass and insulin resistance. To definitively establish the role of adipocyte-PTP1B in body mass regulation and glucose homeostasis, adipocyte-specific-PTP1B knockout mice (adip-crePTP1B(-/-)) were generated using the adiponectin-promoter to drive Cre-recombinase expression. Chow-fed adip-crePTP1B(-/-) mice display enlarged adipocytes, despite having similar body weight/adiposity and glucose homeostasis compared to controls. High-fat diet (HFD)-fed adip-crePTP1B(-/-) mice display no differences in body weight/adiposity but exhibit larger adipocytes, increased circulating glucose and leptin levels, reduced leptin sensitivity and increased basal lipogenesis compared to controls. This is associated with decreased insulin receptor (IR) and Akt/PKB phosphorylation, increased lipogenic gene expression and increased hypoxia-induced factor-1-alpha (Hif-1α) expression. Adipocyte-specific PTP1B deletion does not beneficially manipulate signaling pathways regulating glucose homeostasis, lipid metabolism or adipokine secretion in adipocytes. Moreover, PTP1B does not appear to be the major negative regulator of the IR in adipocytes.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures




Similar articles
-
Liver-specific deletion of protein-tyrosine phosphatase 1B (PTP1B) improves metabolic syndrome and attenuates diet-induced endoplasmic reticulum stress.Diabetes. 2009 Mar;58(3):590-9. doi: 10.2337/db08-0913. Epub 2008 Dec 15. Diabetes. 2009. PMID: 19074988 Free PMC article.
-
Inducible liver-specific knockdown of protein tyrosine phosphatase 1B improves glucose and lipid homeostasis in adult mice.Diabetologia. 2013 Oct;56(10):2286-96. doi: 10.1007/s00125-013-2992-z. Epub 2013 Jul 6. Diabetologia. 2013. PMID: 23832083
-
Wntless regulates lipogenic gene expression in adipocytes and protects against diet-induced metabolic dysfunction.Mol Metab. 2020 Sep;39:100992. doi: 10.1016/j.molmet.2020.100992. Epub 2020 Apr 20. Mol Metab. 2020. PMID: 32325263 Free PMC article.
-
Protein tyrosine phosphatase 1B (PTP1B) and obesity.Vitam Horm. 2013;91:405-24. doi: 10.1016/B978-0-12-407766-9.00017-1. Vitam Horm. 2013. PMID: 23374726 Review.
-
PTP1B and TCPTP--nonredundant phosphatases in insulin signaling and glucose homeostasis.FEBS J. 2013 Jan;280(2):445-58. doi: 10.1111/j.1742-4658.2012.08563.x. Epub 2012 Apr 18. FEBS J. 2013. PMID: 22404968 Review.
Cited by
-
Lessons on conditional gene targeting in mouse adipose tissue.Diabetes. 2013 Mar;62(3):864-74. doi: 10.2337/db12-1089. Epub 2013 Jan 15. Diabetes. 2013. PMID: 23321074 Free PMC article.
-
Norathyriol reverses obesity- and high-fat-diet-induced insulin resistance in mice through inhibition of PTP1B.Diabetologia. 2014 Oct;57(10):2145-54. doi: 10.1007/s00125-014-3315-8. Epub 2014 Jul 2. Diabetologia. 2014. PMID: 24985145
-
Circulating extracellular vesicle-carried PTP1B and PP2A phosphatases as regulators of insulin resistance.Diabetologia. 2025 Jan;68(1):231-242. doi: 10.1007/s00125-024-06288-0. Epub 2024 Oct 18. Diabetologia. 2025. PMID: 39422717 Free PMC article.
-
Deficiency in Protein Tyrosine Phosphatase PTP1B Shortens Lifespan and Leads to Development of Acute Leukemia.Cancer Res. 2018 Jan 1;78(1):75-87. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-17-0946. Epub 2017 Nov 9. Cancer Res. 2018. PMID: 29122767 Free PMC article.
-
Regulation of the SNARE-interacting protein Munc18c tyrosine phosphorylation in adipocytes by protein-tyrosine phosphatase 1B.Cell Commun Signal. 2013 Aug 12;11:57. doi: 10.1186/1478-811X-11-57. Cell Commun Signal. 2013. PMID: 23937695 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

