TNF-α and TGF-β counter-regulate PD-L1 expression on monocytes in systemic lupus erythematosus
- PMID: 22389764
- PMCID: PMC3291882
- DOI: 10.1038/srep00295
TNF-α and TGF-β counter-regulate PD-L1 expression on monocytes in systemic lupus erythematosus
Abstract
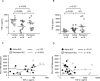
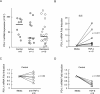
Monocytes in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) are hyperstimulatory for T lymphocytes. We previously found that the normal program for expression of a negative costimulatory molecule programmed death ligand-1 (PD-L1) is defective in SLE patients with active disease. Here, we investigated the mechanism for PD-L1 dysregulation on lupus monocytes. We found that PD-L1 expression on cultured SLE monocytes correlated with TNF-α expression. Exogenous TNF-α restored PD-L1 expression on lupus monocytes. Conversely, TGF-β inversely correlated with PD-L1 in SLE and suppressed expression of PD-L1 on healthy monocytes. Therefore, PD-L1 expression in monocytes is regulated by opposing actions of TNF-α and TGF-β. As PD-L1 functions to fine tune lymphocyte activation, dysregulation of cytokines resulting in reduced expression could lead to loss of peripheral T cell tolerance.
Figures
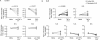


Similar articles
-
The role and clinical significance of programmed cell death- ligand 1 expressed on CD19+B-cells and subsets in systemic lupus erythematosus.Clin Immunol. 2019 Jan;198:89-99. doi: 10.1016/j.clim.2018.11.015. Epub 2018 Nov 28. Clin Immunol. 2019. PMID: 30502542
-
Low expressions of PD-L1 and CTLA-4 by induced CD4+CD25+ Foxp3+ Tregs in patients with SLE and their correlation with the disease activity.Cytokine. 2020 Sep;133:155119. doi: 10.1016/j.cyto.2020.155119. Epub 2020 Jun 11. Cytokine. 2020. PMID: 32535334
-
Enhanced Programmed Death 1 and Diminished Programmed Death Ligand 1 Up-Regulation Capacity of Post-Activated Lupus B Cells.Arthritis Rheumatol. 2019 Sep;71(9):1539-1544. doi: 10.1002/art.40897. Epub 2019 Aug 6. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2019. PMID: 30919595
-
Dual targeting of TGF-β and PD-L1 via a bifunctional anti-PD-L1/TGF-βRII agent: status of preclinical and clinical advances.J Immunother Cancer. 2020 Feb;8(1):e000433. doi: 10.1136/jitc-2019-000433. J Immunother Cancer. 2020. PMID: 32079617 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Therapeutic Potential of Targeting Transforming Growth Factor-beta (TGF-β) and Programmed Death-ligand 1 (PD-L1) in Pancreatic Cancer.Curr Drug Targets. 2023;24(17):1335-1345. doi: 10.2174/0113894501264450231129042256. Curr Drug Targets. 2023. PMID: 38053355 Review.
Cited by
-
Perspectives on immune checkpoint ligands: expression, regulation, and clinical implications.BMB Rep. 2021 Aug;54(8):403-412. doi: 10.5483/BMBRep.2021.54.8.054. BMB Rep. 2021. PMID: 34078531 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Generation, secretion and degradation of cancer immunotherapy target PD-L1.Cell Mol Life Sci. 2022 Jul 11;79(8):413. doi: 10.1007/s00018-022-04431-x. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2022. PMID: 35819633 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Targeting TNFR2: A Novel Breakthrough in the Treatment of Cancer.Front Oncol. 2022 Apr 14;12:862154. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2022.862154. eCollection 2022. Front Oncol. 2022. PMID: 35494080 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Therapeutic polyclonal human CD8+ CD25+ Fox3+ TNFR2+ PD-L1+ regulatory cells induced ex-vivo.Clin Immunol. 2013 Dec;149(3):450-63. doi: 10.1016/j.clim.2013.08.007. Epub 2013 Aug 20. Clin Immunol. 2013. PMID: 24211847 Free PMC article.
-
Immuno-Contexture and Immune Checkpoint Molecule Expression in Mismatch Repair Proficient Colorectal Carcinoma.Cancers (Basel). 2023 Jun 7;15(12):3097. doi: 10.3390/cancers15123097. Cancers (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37370706 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Blanco P., Palucka A. K., Gill M., Pascual V. & Banchereau J. Induction of dendritic cell differentiation by IFN-alpha in systemic lupus erythematosus. Science 294, 1540–1543 (2001). - PubMed
-
- Katsiari C. G., Liossis S. N. & Sfikakis P. P. The Pathophysiologic Role of Monocytes and Macrophages in Systemic Lupus Erythematosus: A Reappraisal. Semin Arthritis Rheum 39, 491–503 (2009). - PubMed
-
- Ding D., Mehta H., McCune W. J. & Kaplan M. J. Aberrant phenotype and function of myeloid dendritic cells in systemic lupus erythematosus. J Immunol 177, 5878–5889 (2006). - PubMed
-
- Monrad S. & Kaplan M. J. Dendritic cells and the immunopathogenesis of systemic lupus erythematosus. Immunol Res 37, 135–145 (2007). - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

