Assessment of extracts from red yeast rice for herb-drug interaction by in-vitro and in-vivo assays
- PMID: 22389767
- PMCID: PMC3291881
- DOI: 10.1038/srep00298
Assessment of extracts from red yeast rice for herb-drug interaction by in-vitro and in-vivo assays
Abstract
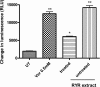
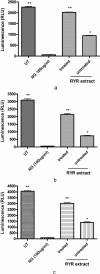
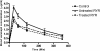
Red yeast rice (RYR) is made by fermenting the yeast Monascus purpureus over rice. It is a source of natural red food colorants, a food garnish and a traditional medication. Results of the current study demonstrated that polar fractions of the RYR preparations contained herbal-drug interaction activity, which if left unremoved, enhanced P-glycoprotein activity and inhibited the major drug metabolizing cytochromes P450, i,e, CYP 1A2, 2C9 and 3A4. The data from Caco-2 cell absorption and animal model studies further demonstrated that the pharmacokinetic modulation effect by RYR preparations containing the polar fractions ("untreated" preparation) was greater than that from RYR preparations with the polar fractions removed ("treated" preparation). The data indicates a potential for herb-drug interactions to be present in RYR commonly sold as nutritional supplements when the polar fractions are not removed and this should be taken into consideration when RYR is consumed with medications, including verapamil.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Anticancer effects of Chinese red yeast rice versus monacolin K alone on colon cancer cells.J Nutr Biochem. 2008 Jul;19(7):448-58. doi: 10.1016/j.jnutbio.2007.05.012. Epub 2007 Sep 14. J Nutr Biochem. 2008. PMID: 17869085 Free PMC article.
-
Functional food red yeast rice (RYR) for metabolic syndrome amelioration: a review on pros and cons.World J Microbiol Biotechnol. 2016 May;32(5):87. doi: 10.1007/s11274-016-2035-2. Epub 2016 Apr 2. World J Microbiol Biotechnol. 2016. PMID: 27038957 Review.
-
Chinese red yeast rice versus lovastatin effects on prostate cancer cells with and without androgen receptor overexpression.J Med Food. 2008 Dec;11(4):657-66. doi: 10.1089/jmf.2007.0702. J Med Food. 2008. PMID: 19053857
-
Red yeast rice for the treatment of dyslipidemia.Curr Atheroscler Rep. 2015 Apr;17(4):495. doi: 10.1007/s11883-015-0495-8. Curr Atheroscler Rep. 2015. PMID: 25728312 Review.
-
Chemical profiling and quantification of monacolins and citrinin in red yeast rice commercial raw materials and dietary supplements using liquid chromatography-accurate QToF mass spectrometry: Chemometrics application.J Pharm Biomed Anal. 2014 Nov;100:243-253. doi: 10.1016/j.jpba.2014.07.039. Epub 2014 Aug 9. J Pharm Biomed Anal. 2014. PMID: 25168220
Cited by
-
Peripheral neuropathy induced by red yeast rice in a patient with a known small bowel gastrointestinal tumour.BMJ Case Rep. 2013 Apr 5;2013:bcr2013009060. doi: 10.1136/bcr-2013-009060. BMJ Case Rep. 2013. PMID: 23563686 Free PMC article.
-
Red Yeast Rice: A Systematic Review of the Traditional Uses, Chemistry, Pharmacology, and Quality Control of an Important Chinese Folk Medicine.Front Pharmacol. 2019 Dec 2;10:1449. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2019.01449. eCollection 2019. Front Pharmacol. 2019. PMID: 31849687 Free PMC article.
-
PharmActa: Empowering Patients to Avoid Clinical Significant Drug⁻Herb Interactions.Medicines (Basel). 2019 Feb 16;6(1):26. doi: 10.3390/medicines6010026. Medicines (Basel). 2019. PMID: 30781500 Free PMC article.
-
Interaction between phytotherapy and oral anticancer agents: prospective study and literature review.Med Oncol. 2019 Apr 16;36(5):45. doi: 10.1007/s12032-019-1267-z. Med Oncol. 2019. PMID: 30993543 Review.
-
Synergistic Effects of Plant Derivatives and Conventional Chemotherapeutic Agents: An Update on the Cancer Perspective.Medicina (Kaunas). 2019 Apr 17;55(4):110. doi: 10.3390/medicina55040110. Medicina (Kaunas). 2019. PMID: 30999703 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Heber D., Lembertas A., Lu Q. Y., Bowerman S. & Liang V. An Analysis of Nine Proprietary Chinese Red Yeast Rice Dietary Supplements: Implications of Variability in Chemical Profile and Contents. J Altern Complement Med. 7, 231–236 (2001). - PubMed
-
- Ma J. et al. Constituents of red yeast rice, a traditional Chinese food and medicine. J Agric Food Chem. 48, 5220–5225 (2000). - PubMed
-
- Heber D. Dietary supplement or drug? The case for cholestin. Am J Clin Nutr. 70,106–108 (1999). - PubMed
-
- Lin Y. L., Wang T. H., Lee M. H. & Su N. W. Biologically active components and nutraceuticals in the Monascus-fermented rice: a review. Appl Micorbiol and Biotechnol. 77, 965–973 (2008). - PubMed
-
- Retterstøl K., Stugaard M., Gørbitz C., & Ose L. Results of intensive long-term treatment of familial hypercholesterolemia. Am J Cardio. 78, 1369–1374 (1996). - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

