Multimodal behavior program for ADHD incorporating yoga and implemented by high school volunteers: a pilot study
- PMID: 22389788
- PMCID: PMC3263567
- DOI: 10.5402/2011/780745
Multimodal behavior program for ADHD incorporating yoga and implemented by high school volunteers: a pilot study
Abstract
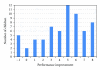
A low-cost resource approach to ADHD therapy would be a practical approach to treating children in developing countries. Research has shown that ADHD is prevalent in all areas of the world, and yet treatment for children in more impoverished countries is still lacking. The approach taken was to combine yoga and meditation combined with multimodal behavioral therapy program for children ageing 6 to 11. The program was kept low cost by using trained high school volunteers and integrating the program within the public school. After 6 weeks of the program, 90.5% of children showed improvement as measured by their performance impairment score, a measurement of academic performance. Parent and Teacher evaluations of behavior also found improvement as 25 of the 64 children (39.1%) improved into the normal range as measured by the Vanderbilt questionnaire. Moreover, children could successfully learn both yoga and meditation from high school students irrespective of their age, ADHD type, or initial performance impairment. The results demonstrate efficacy of a multimodal behavioral program incorporating yoga and meditation. The use of high school volunteers from schools in the area demonstrates an effective low-cost and universally applicable approach.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Peer-mediated multimodal intervention program for the treatment of children with ADHD in India: one-year followup.ISRN Pediatr. 2012;2012:419168. doi: 10.5402/2012/419168. Epub 2012 Dec 20. ISRN Pediatr. 2012. PMID: 23316384 Free PMC article.
-
A process for developing community consensus regarding the diagnosis and management of attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder.Pediatrics. 2005 Jan;115(1):e97-104. doi: 10.1542/peds.2004-0953. Pediatrics. 2005. PMID: 15629972
-
Relaxation response-based yoga improves functioning in young children with autism: a pilot study.J Altern Complement Med. 2011 Nov;17(11):1029-35. doi: 10.1089/acm.2010.0834. Epub 2011 Oct 12. J Altern Complement Med. 2011. PMID: 21992466 Free PMC article.
-
2013 SYR Accepted Poster Abstracts.Int J Yoga Therap. 2013;23 Suppl:32-53. Int J Yoga Therap. 2013. PMID: 24176784 Clinical Trial.
-
School-based Yoga Programs in the United States: A Survey.Adv Mind Body Med. 2015 Fall;29(4):18-26. Adv Mind Body Med. 2015. PMID: 26535474 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Effects of Combining Meditation Techniques on Short-Term Memory, Attention, and Affect in Healthy College Students.Front Psychol. 2021 Mar 5;12:607573. doi: 10.3389/fpsyg.2021.607573. eCollection 2021. Front Psychol. 2021. PMID: 33746830 Free PMC article.
-
Mindfulness Meditation Training for Attention-Deficit/Hyperactivity Disorder in Adulthood: Current Empirical Support, Treatment Overview, and Future Directions.Cogn Behav Pract. 2015 May;22(2):172-191. doi: 10.1016/j.cbpra.2014.10.002. Cogn Behav Pract. 2015. PMID: 25908900 Free PMC article.
-
Yoga May Mitigate Decreases in High School Grades.Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2015;2015:259814. doi: 10.1155/2015/259814. Epub 2015 Aug 10. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2015. PMID: 26347787 Free PMC article.
-
Scoping Review of Yoga in Schools: Mental Health and Cognitive Outcomes in Both Neurotypical and Neurodiverse Youth Populations.Children (Basel). 2022 Jun 8;9(6):849. doi: 10.3390/children9060849. Children (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35740786 Free PMC article.
-
A Virtual Reality Game (The Secret Trail of Moon) for Treating Attention-Deficit/Hyperactivity Disorder: Development and Usability Study.JMIR Serious Games. 2021 Sep 1;9(3):e26824. doi: 10.2196/26824. JMIR Serious Games. 2021. PMID: 34468332 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Polanczyk G, de Lima MS, Horta BL, Biederman J, Rohde LA. The worldwide prevalence of ADHD: a systematic review and metaregression analysis. American Journal of Psychiatry. 2007;164(6):942–948. - PubMed
-
- Froehlich TE, Lanphear BP, Epstein JN, Barbaresi WJ, Katusic SK, Kahn RS. Prevalence, recognition, and treatment of attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder in a national sample of US children. Archives of Pediatrics and Adolescent Medicine. 2007;161(9):857–864. - PubMed
-
- Kaur P, Chavan BS, Lata S, et al. Early intervention in developmental delay. Indian Journal of Pediatrics. 2006;73(5):405–408. - PubMed
-
- Mukhopadhyay M, Misra S, Mitra T, Niyogi P. Attention deficit hyperactivity disorder. Indian Journal of Pediatrics. 2003;70(10):789–792. - PubMed
-
- Bhatia MS, Nigam VR, Bohra N, Malik SC. Attention deficit disorder with hyperactivity among paediatric outpatients. Journal of Child Psychology and Psychiatry and Allied Disciplines. 1991;32(2):297–306. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

