Molecular characterization of neuroendocrine prostate cancer and identification of new drug targets
- PMID: 22389870
- PMCID: PMC3290518
- DOI: 10.1158/2159-8290.CD-11-0130
Molecular characterization of neuroendocrine prostate cancer and identification of new drug targets
Abstract
Neuroendocrine prostate cancer (NEPC) is an aggressive subtype of prostate cancer that most commonly evolves from preexisting prostate adenocarcinoma (PCA). Using Next Generation RNA-sequencing and oligonucleotide arrays, we profiled 7 NEPC, 30 PCA, and 5 benign prostate tissue (BEN), and validated findings on tumors from a large cohort of patients (37 NEPC, 169 PCA, 22 BEN) using IHC and FISH. We discovered significant overexpression and gene amplification of AURKA and MYCN in 40% of NEPC and 5% of PCA, respectively, and evidence that that they cooperate to induce a neuroendocrine phenotype in prostate cells. There was dramatic and enhanced sensitivity of NEPC (and MYCN overexpressing PCA) to Aurora kinase inhibitor therapy both in vitro and in vivo, with complete suppression of neuroendocrine marker expression following treatment. We propose that alterations in Aurora kinase A and N-myc are involved in the development of NEPC, and future clinical trials will help determine from the efficacy of Aurora kinase inhibitor therapy.
Significance: We report on the largest in-depth molecular analysis of NEPC and provide new insight into molecular events involved in the progression of prostate cancer.
Keywords: aurora kinase A; drug targets; n-myc; neuroendocrine prostate cancer.
© 2011 AACR.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
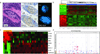
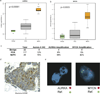
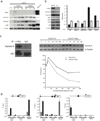
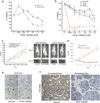
Comment in
-
Understanding the lethal variant of prostate cancer: power of examining extremes.Cancer Discov. 2011 Nov;1(6):466-8. doi: 10.1158/2159-8290.CD-11-0259. Cancer Discov. 2011. PMID: 22586648 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Palmgren JS, Karavadia SS, Wakefield MR. Unusual and underappreciated: small cell carcinoma of the prostate. Semin Oncol. 2007;34:22–29. - PubMed
-
- Wang W, Epstein JI. Small cell carcinoma of the prostate. A morphologic and immunohistochemical study of 95 cases. Am J Surg Pathol. 2008;32:65–71. - PubMed
-
- Tomlins SA, Rhodes DR, Perner S, Dhanasekaran SM, Mehra R, Sun XW, et al. Recurrent fusion of TMPRSS2 and ETS transcription factor genes in prostate cancer. Science. 2005;310:644–648. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

