Cell-selective inhibition of NF-κB signaling improves therapeutic index in a melanoma chemotherapy model
- PMID: 22389871
- PMCID: PMC3290412
- DOI: 10.1158/2159-8290.CD-11-0143
Cell-selective inhibition of NF-κB signaling improves therapeutic index in a melanoma chemotherapy model
Abstract
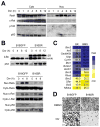
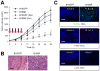
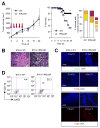
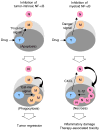
The transcription factor NF-κB promotes survival of cancer cells exposed to doxorubicin and other chemotherapeutic agents. IκB kinase is essential for chemotherapy-induced NF-κB activation and considered a prime target for anticancer treatment. An IκB kinase inhibitor sensitized human melanoma xenografts in mice to killing by doxorubicin, yet also exacerbated treatment toxicity in the host animals. Using mouse models that simulate cell-selective targeting, we found that impaired NF-κB activation in melanoma and host myeloid cells accounts for the therapeutic and the adverse effects, respectively. Ablation of tumor-intrinsic NF-κB activity resulted in apoptosis-driven tumor regression following doxorubicin treatment. By contrast, chemotherapy in mice with myeloid-specific loss of NF-κB activation led to a massive intratumoral recruitment of interleukin-1β-producing neutrophils and necrotic tumor lesions, a condition associated with increased host mortality but not accompanied by tumor regression. Therefore, a molecular target-based therapy may be steered toward different clinical outcomes depending on the drug's cell-specific effects.
Significance: Our findings show that the IκB kinase–NF-κB signaling pathway is important for both promoting treatment resistance and preventing host toxicity in cancer chemotherapy; however, the two functions are exerted by distinct cell type–specific mechanisms and can therefore be selectively targeted to achieve an improved therapeutic outcome.
Keywords: NF-κB; efficacy; melanoma; neutrophil; toxicity.
© 2011 AACR.
Figures



Comment in
-
NF-κB in cancer: a matter of life and death.Cancer Discov. 2011 Nov;1(6):469-71. doi: 10.1158/2159-8290.CD-11-0260. Cancer Discov. 2011. PMID: 22586649 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Savage P, Stebbing J, Bower M, Crook T. Why does cytotoxic chemotherapy cure only some cancers? Nat Clin Pract Oncol. 2009;6:43–52. - PubMed
-
- Cotter TG. Apoptosis and cancer: the genesis of a research field. Nat Rev Cancer. 2009;9:501–7. - PubMed
-
- Paulus P, Stanley ER, Schäfer R, Abraham D, Aharinejad S. Colony-stimulating factor-1 antibody reverses chemoresistance in human MCF-7 breast cancer xenografts. Cancer Res. 2006;66:4349–56. - PubMed
-
- Ghiringhelli F, Apetoh L, Tesniere A, Aymeric L, Ma Y, Ortiz C, et al. Activation of the NLRP3 inflammasome in dendritic cells induces IL-1β-dependent adaptive immunity against tumors. Nat Med. 2009;15:1170–8. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

