Palmitoylation of Hedgehog proteins
- PMID: 22391306
- PMCID: PMC4214369
- DOI: 10.1016/B978-0-12-394622-5.00010-9
Palmitoylation of Hedgehog proteins
Abstract
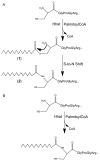
Hedgehog (Hh) proteins are secreted signaling proteins that contain amide-linked palmitate at the N-terminus and cholesterol at the C-terminus. Palmitoylation of Hh proteins is critical for effective long- and short-range signaling. The palmitoylation reaction occurs during transit of Hh through the secretory pathway, most likely in the lumen of the ER. Attachment of palmitate to Hh proteins is independent of cholesterol modification and autoprocessing and is catalyzed by Hhat (Hedgehog acyltransferase). Hhat is a member of the membrane bound O-acyltransferase (MBOAT) family, a subgroup of multipass membrane proteins that catalyze transfer of fatty acyl groups to lipids and proteins. Several classes of secreted proteins have recently been shown to be substrates for MBOAT acyltransferases, including Hh proteins and Spitz (palmitoylated by Hhat), Wg/Wnt proteins (modified with palmitate and/or palmitoleate by Porcupine) and ghrelin (octanoylated by ghrelin O-acyltransferase). These findings highlight protein fatty acylation as a mechanism that not only influences membrane binding of intracellular proteins but also regulates the signaling range and efficacy of secreted proteins.
Copyright © 2012 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures

References
-
- Alland L, Peseckis SM, Atherton RE, Berthiaume L, Resh MD. Dual myristylation and palmitoylation of Src family member p59fyn affects subcellular localization. J. Biol. Chem. 1994;269:16701–16705. - PubMed
-
- Amanai K, Jiang J. Distinct roles of Central missing and Dispatched in sending the Hedgehog signal. Development. 2001;128:5119–5127. - PubMed
-
- Arcaro A, Gregoire C, Bakker TR, Baldi L, Jordan M, Goffin L, Boucheron N, Wurm F, van der Merwe PA, Malissen B, Luescher IF. CD8beta endows CD8 with efficient coreceptor function by coupling T cell receptor/CD3 to raft- associated CD8/p56(lck) complexes. J. Exp. Med. 2001;194:1485–1495. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Beachy PA, Karhadkar SS, Berman DM. Tissue repair and stem cell renewal in carcinogenesis. Nature. 2004;432:324–331. - PubMed
-
- Bellaiche Y, The I, Perrimon N. Tout-velu is a Drosophila homologue of the putative tumour suppressor EXT-1 and is needed for Hh diffusion. Nature. 1998;394:85–88. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

