CYP2D6 and UGT2B7 genotype and risk of recurrence in tamoxifen-treated breast cancer patients
- PMID: 22395643
- PMCID: PMC3611934
- DOI: 10.1093/jnci/djs126
CYP2D6 and UGT2B7 genotype and risk of recurrence in tamoxifen-treated breast cancer patients
Erratum in
- J Natl Cancer Inst. 2012 Nov 21;104(22):1772
Abstract
Background: Adjuvant tamoxifen therapy substantially decreases the risk of recurrence and mortality in women with hormone (estrogen and/or progesterone) receptor-positive breast cancer. Previous studies have suggested that metabolic conversion of tamoxifen to endoxifen by cytochrome P450 2D6 (CYP2D6) is required for patient benefit from tamoxifen therapy.
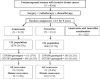
Methods: Tumor specimens from a subset of postmenopausal patients with hormone receptor-positive early-stage (stages I, II, and IIIA) breast cancer, who were enrolled in the randomized double-blind Arimidex, Tamoxifen, Alone or in Combination (ATAC) clinical trial, were genotyped for variants in CYP2D6 (N = 1203 patients: anastrozole [trade name: Arimidex] group, n = 615 patients; tamoxifen group, n = 588 patients) and UDP-glucuronosyltransferase-2B7 (UGT2B7), whose gene product inactivates endoxifen (N = 1209 patients; anastrozole group, n = 606 patients; tamoxifen group, n = 603 patients). Genotyping was performed using polymerase chain reaction-based TaqMan assays. Based on the genotypes for CYP2D6, patients were classified as poor metabolizer (PM), intermediate metabolizer (IM), or extensive metabolizer (EM) phenotypes. We evaluated the association of CYP2D6 and UGT2B7 genotype with distant recurrence (primary endpoint) and any recurrence (secondary endpoint) by estimating the hazard ratios (HRs) and corresponding 95% confidence intervals (CIs) using Cox proportional hazards models. All statistical tests were two-sided.
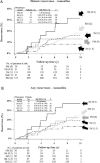
Results: After a median follow-up of 10 years, no statistically significant associations were observed between CYP2D6 genotype and recurrence in tamoxifen-treated patients (PM vs EM: HR for distant recurrence = 1.25, 95% CI = 0.55 to 3.15, P = .64; HR for any recurrence = 0.99, 95% CI = 0.48 to 2.08, P = .99). A near-null association was observed between UGT2B7 genotype and recurrence in tamoxifen-treated patients. No associations were observed between CYP2D6 and UGT2B7 genotypes and recurrence in anastrozole-treated patients.
Conclusion: The results do not support the hypothesis that CYP2D6 genotype predicts clinical benefit of adjuvant tamoxifen treatment among postmenopausal breast cancer patients.
Figures
Comment in
-
CYP2D6 genotype as a marker for benefit of adjuvant tamoxifen in postmenopausal women: lessons learned.J Natl Cancer Inst. 2012 Mar 21;104(6):427-8. doi: 10.1093/jnci/djs139. Epub 2012 Mar 6. J Natl Cancer Inst. 2012. PMID: 22395645 No abstract available.
-
Re: CYP2D6 genotype and tamoxifen response in postmenopausal women with endocrine-responsive breast cancer: the Breast International Group 1-98 trial.J Natl Cancer Inst. 2012 Aug 22;104(16):1265-6; author reply 1266-8. doi: 10.1093/jnci/djs305. Epub 2012 Jul 31. J Natl Cancer Inst. 2012. PMID: 22851267 No abstract available.
-
Re: CYP2D6 genotype and tamoxifen response in postmenopausal women with endocrine-responsive breast cancer: the Breast International Group 1-98 trial and Re: CYP2D6 and UGT2B7 genotype and risk of recurrence in tamoxifen-treated breast cancer patients.J Natl Cancer Inst. 2012 Aug 22;104(16):1263-4; author reply 1266-8. doi: 10.1093/jnci/djs312. Epub 2012 Jul 31. J Natl Cancer Inst. 2012. PMID: 22851268 No abstract available.
-
Re: CYP2D6 genotype and tamoxifen response in postmenopausal women with endocrine-responsive breast cancer: the Breast International Group 1-98 trial.J Natl Cancer Inst. 2012 Aug 22;104(16):1264; author reply 1266-8. doi: 10.1093/jnci/djs304. Epub 2012 Jul 31. J Natl Cancer Inst. 2012. PMID: 22851270 No abstract available.
References
-
- Early Breast Cancer Trialists’ Collaborative Group (EBCTCG) Effects of chemotherapy and hormonal therapy for early breast cancer on recurrence and 15-year survival: an overview of the randomised trials. Lancet. 2005;365(9472):1687–1717. - PubMed
-
- Stearns V, Johnson MD, Rae JM, et al. Active tamoxifen metabolite plasma concentrations after coadministration of tamoxifen and the selective serotonin reuptake inhibitor paroxetine. J Natl Cancer Inst. 2003;95(23):1758–1764. - PubMed
-
- Desta Z, Ward BA, Soukhova NV, Flockhart DA. Comprehensive evaluation of tamoxifen sequential biotransformation by the human cytochrome P450 system in vitro: prominent roles for CYP3A and CYP2D6. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2004;310(3):1062–1075. - PubMed
-
- Jin Y, Desta Z, Stearns V, et al. CYP2D6 genotype, antidepressant use, and tamoxifen metabolism during adjuvant breast cancer treatment. J Natl Cancer Inst. 2005;97(1):30–39. - PubMed
-
- Johnson MD, Zuo H, Lee KH, et al. Pharmacological characterization of 4-hydroxy- N -desmethyl tamoxifen, a novel active metabolite of tamoxifen. Breast Cancer Res Treat. 2004;85(2):151–159. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

