Biglycan is an extracellular MuSK binding protein important for synapse stability
- PMID: 22396407
- PMCID: PMC3313673
- DOI: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.4610-11.2012
Biglycan is an extracellular MuSK binding protein important for synapse stability
Abstract
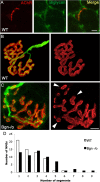
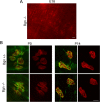
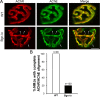
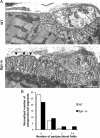
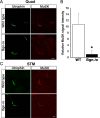
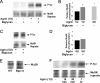
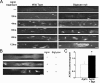
The receptor tyrosine kinase MuSK is indispensable for nerve-muscle synapse formation and maintenance. MuSK is necessary for prepatterning of the endplate zone anlage and as a signaling receptor for agrin-mediated postsynaptic differentiation. MuSK-associated proteins such as Dok7, LRP4, and Wnt11r are involved in these early events in neuromuscular junction formation. However, the mechanisms regulating synapse stability are poorly understood. Here we examine a novel role for the extracellular matrix protein biglycan in synapse stability. Synaptic development in fetal and early postnatal biglycan null (bgn(-/o)) muscle is indistinguishable from wild-type controls. However, by 5 weeks after birth, nerve-muscle synapses in bgn(-/o) mice are abnormal as judged by the presence of perijunctional folds, increased segmentation, and focal misalignment of acetylcholinesterase and AChRs. These observations indicate that previously occupied presynaptic and postsynaptic territory has been vacated. Biglycan binds MuSK and the levels of this receptor tyrosine kinase are selectively reduced at bgn(-/o) synapses. In bgn(-/o) myotubes, the initial stages of agrin-induced MuSK phosphorylation and AChR clustering are normal, but the AChR clusters are unstable. This stability defect can be substantially rescued by the addition of purified biglycan. Together, these results indicate that biglycan is an extracellular ligand for MuSK that is important for synapse stability.
Figures

References
-
- Ameye L, Young MF. Mice deficient in small leucine-rich proteoglycans: novel in vivo models for osteoporosis, osteoarthritis, Ehlers-Danlos syndrome, muscular dystrophy, and corneal diseases. Glycobiology. 2002;12:107R–116R. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- R44 NS045432/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- RR15578/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- T32 MH020068/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- AR42826/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- T32 GM007601/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- AG05917/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HD023924/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- K12 HD000850/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AG005917/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AR042826/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- U01 NS064295/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- HD00850/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- P20 RR015578/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- HD23924/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- ImNIH/Intramural NIH HHS/United States
- T32GM007601/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous
