New enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay for detection of antibodies against hepatitis delta virus using a hepatitis delta antigen derived from a Taiwanese clone and comparison to the Abbott radioimmunoassay
- PMID: 22398247
- PMCID: PMC3346331
- DOI: 10.1128/CVI.05687-11
New enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay for detection of antibodies against hepatitis delta virus using a hepatitis delta antigen derived from a Taiwanese clone and comparison to the Abbott radioimmunoassay
Abstract
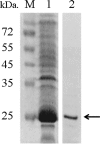
An anti-hepatitis delta (HD) enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) using a specific recombinant hepatitis delta antigen derived from a local dominant hepatitis delta virus (hepatitis D virus; HDV) strain in Taiwan has been established. The detection efficiency of this assay was comparable to that of the commercially available Abbott anti-HD radioimmunoassay (RIA) and could be useful in routine laboratory diagnoses of HDV infection.
Figures
Similar articles
-
High expression of small hepatitis D antigen in Escherichia coli and ELISA for diagnosis of hepatitis D virus.J Virol Methods. 2014 Mar;197:34-8. doi: 10.1016/j.jviromet.2013.10.006. Epub 2013 Oct 16. J Virol Methods. 2014. PMID: 24140186
-
Development of a hepatitis delta virus antibody assay for study of the prevalence of HDV among individuals infected with hepatitis B virus in China.J Med Virol. 2012 Mar;84(3):445-9. doi: 10.1002/jmv.23212. J Med Virol. 2012. PMID: 22246830
-
[Detection of HDV antigen and antibody].Nihon Rinsho. 2004 Aug;62 Suppl 8:412-5. Nihon Rinsho. 2004. PMID: 15453357 Review. Japanese. No abstract available.
-
A universal point-of-care immunochromatographic test for the serodiagnosis of hepatitis D.J Clin Microbiol. 2025 May 14;63(5):e0199924. doi: 10.1128/jcm.01999-24. Epub 2025 Apr 11. J Clin Microbiol. 2025. PMID: 40214253 Free PMC article.
-
Hepatitis delta virus: the molecular basis of laboratory diagnosis.Crit Rev Clin Lab Sci. 2000 Feb;37(1):45-92. doi: 10.1080/10408360091174178. Crit Rev Clin Lab Sci. 2000. PMID: 10737440 Review.
Cited by
-
Proteins and peptides as antigen candidates for the immunodiagnosis of hepatitis D.Amino Acids. 2025 Jul 4;57(1):35. doi: 10.1007/s00726-025-03465-2. Amino Acids. 2025. PMID: 40613912 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A comprehensive review of diagnostic approaches for hepatitis D.Front Mol Biosci. 2025 May 21;12:1598784. doi: 10.3389/fmolb.2025.1598784. eCollection 2025. Front Mol Biosci. 2025. PMID: 40469079 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Comparison of Enzyme Immunoassays for Detection of Antibodies to Hepatitis D Virus in Serum.Clin Vaccine Immunol. 2016 Aug 5;23(8):732-4. doi: 10.1128/CVI.00028-16. Print 2016 Aug. Clin Vaccine Immunol. 2016. PMID: 27280621 Free PMC article.
-
Assessing the diagnostic accuracy of serological tests for hepatitis delta virus diagnosis: a systematic review and meta-analysis.Sci Rep. 2024 Aug 9;14(1):18475. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-69304-8. Sci Rep. 2024. PMID: 39122751 Free PMC article.
-
Improving Access to Anti-HDV Testing: Development and Validation of an Affordable In-House ELISA Assay.ACS Omega. 2024 Apr 5;9(15):17137-17142. doi: 10.1021/acsomega.3c09843. eCollection 2024 Apr 16. ACS Omega. 2024. PMID: 38645367 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Chen DS, Lai MY, Sung JL. 1984. Delta agent infection in patients with chronic liver diseases and hepatocellular carcinoma—an infrequent finding in Taiwan. Hepatology 4:502–503 - PubMed
-
- Deny P. 2006. Hepatitis delta virus genetic variability: from genotypes I, II, III to eight major clades? Curr. Top. Microbiol. Immunol. 307:151–171 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical