Apolipoprotein e genotype-dependent paradoxical short-term effects of (56)fe irradiation on the brain
- PMID: 22401921
- PMCID: PMC3742074
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ijrobp.2011.12.049
Apolipoprotein e genotype-dependent paradoxical short-term effects of (56)fe irradiation on the brain
Abstract
Purpose: In humans, apolipoprotein E (apoE) is encoded by three major alleles (ε2, ε3, and ε4) and, compared to apoE3, apoE4 increases the risk of developing Alzheimer disease and cognitive impairments following various environmental challenges. Exposure to irradiation, including that of (56)Fe, during space missions poses a significant risk to the central nervous system, and apoE isoform might modulate this risk.
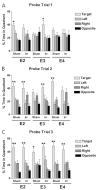
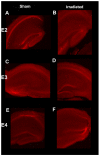
Methods and materials: We investigated whether apoE isoform modulates hippocampus-dependent cognitive performance starting 2 weeks after (56)Fe irradiation. Changes in reactive oxygen species (ROS) can affect cognition and are induced by irradiation. Therefore, after cognitive testing, we assessed hippocampal ROS levels in ex vivo brain slices, using the ROS-sensitive fluorescent probe, dihydroethidium (DHE). Brain levels of 3-nitrotyrosine (3-NT), CuZn superoxide dismutase (CuZnSOD), extracellular SOD, and apoE were assessed using Western blotting analysis.
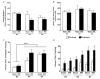
Results: In the water maze, spatial memory retention was impaired by irradiation in apoE2 and apoE4 mice but enhanced by irradiation in apoE3 mice. Irradiation reduced DHE-oxidation levels in the enclosed blade of the dentate gyrus and levels of 3-NT and CuZnSOD in apoE2 but not apoE3 or apoE4 mice. Finally, irradiation increased apoE levels in apoE3 but not apoE2 or apoE4 mice.
Conclusions: The short-term effects of (56)Fe irradiation on hippocampal ROS levels and hippocampus-dependent spatial memory retention are apoE isoform-dependent.
Copyright © 2012 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures



References
-
- Raber J. Unintended effects of cranial irradiation on cognitive function. Toxicol Pathol. 2010;38(1):198–202. - PubMed
-
- Manda K, Ueno M, Anzai K. Space radiation-induced inhibition of neurogenesis in the hippocampal dentate gyrus and memory impairment in mice: ameliorative potential of the melatonin metabolite, AFMK. J Pineal Res. 2008;45(4):430–438. - PubMed
-
- Poirier J. Apolipoprotein E in animal models of CNS injury and in Alzheimer’s disease. Trends Neurosci. 1994;17(12):525–530. - PubMed
-
- Higuchi Y, Nelson GA, Vazquez M, et al. Apolipoprotein E expression and behavioral toxicity of high charge, high energy (HZE) particle radiation. J Radiat Res (Tokyo) 2002;43(Suppl):S219–S224. - PubMed
-
- Villasana LE, Benice TS, Raber J. Long-term effects of 56Fe irradiation on spatial memory of mice: Role of sex and apolipoprotein E isoform. Int J Radiat Oncol. 2010;80:567–573. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

