Alcohol consumption and premotor corpus callosum in older adults
- PMID: 22401959
- PMCID: PMC3378772
- DOI: 10.1016/j.euroneuro.2012.02.003
Alcohol consumption and premotor corpus callosum in older adults
Abstract
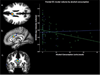
Heavy alcohol consumption is toxic to the brain, especially to the frontal white matter (WM), but whether lesser amounts of alcohol negatively impact the brain WM is unclear. In this study, we examined the relationship between self-reported alcohol consumption and regional WM and grey matter (GM) volume in fifty-six men and thirty-seven women (70+- 7years) cognitively intact participants of the Baltimore Longitudinal Study of Aging (BLSA) with no history of alcohol abuse. We used regional analysis of volumes examined in normalized space (RAVENS) maps methodology for WM and GM segmentation and normalization followed by voxel based morphometry (VBM) implemented in SPM8 to examine the cross-sectional association between alcohol consumption and regional WM (and, separately, GM) volume controlling for age, sex, smoking, blood pressure and dietary thiamine intake. WM VBM revealed that in men, but not in women, higher alcohol consumption was associated with lower volume in premotor frontal corpus callosum. This finding suggests that even moderate amounts of alcohol may be detrimental to corpus callosum and white matter integrity.
Published by Elsevier B.V.
Conflict of interest statement
All authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Anstey KJ, Mack HA, Cherbuin N. Alcohol consumption as a risk factor for dementia and cognitive decline: meta-analysis of prospective studies. Am J Geriatr Psychiatry. 2009;17(7):542–555. - PubMed
-
- Ashburner J, Friston KJ. Voxel-based morphometry--the methods. Neuroimage. 2000;11(6 Pt 1):805–821. - PubMed
-
- Babor TF, Steinberg K, Anton R, Del Boca F. Talk is cheap: measuring drinking outcomes in clinical trials. J Stud Alcohol. 2000;61(1):55–63. - PubMed
-
- Bartsch AJ, Homola G, Biller A, Smith SM, et al. Manifestations of early brain recovery associated with abstinence from alcoholism. Brain. 2007;130(Pt 1):36–47. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

