The clinical value of in vivo confocal microscopy for diagnosis of ocular surface squamous neoplasia
- PMID: 22402703
- PMCID: PMC3376276
- DOI: 10.1038/eye.2012.15
The clinical value of in vivo confocal microscopy for diagnosis of ocular surface squamous neoplasia
Abstract
Purpose: To determine the reliability and efficiency of in vivo confocal microscopy for the diagnosis of ocular surface squamous neoplasia (OSSN).
Methods: A case series with five consecutive cases of OSSN were investigated retrospectively, of which the characteristics and subspecial types had been estimated by in vivo confocal microscopy before surgery. The structure and cellular features of OSSN were analyzed with other examinations, such as anterior-segment optical coherence tomography (AS-OCT), and confirmed by histopathological biopsy.
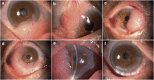
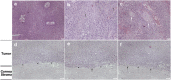
Results: The tumors revealed red gelatinous surfaces with vascular dilatation on the ocular surface of the conjunctival and corneal epithelium in anterior segment photography. Involvement of only corneal epithelium was observed by AS-OCT in three cases, whereas the Bowman's layer and anterior stroma were also invaded in the other two cases. In vivo confocal microscopy showed cellular anisocytosis and enlarged nuclei with high nuclear to cytoplasmic ratio in three cases diagnosed as conjunctival intraepithelial neoplasia; moreover, nests were partially formed by isolated keratinized, binucleated, and actively mitotic dysmorphic epithelial cells in the other two cases diagnosed as carcinoma in situ and ocular surface squamous carcinoma (OSSC). The characteristics assessed from histopathological biopsy were similar to that revealed by in vivo confocal microscopy in all five cases.
Conclusion: In vivo confocal microscopy analysis of cytological characteristics of OSSN is a safe, relatively noninvasive, and effective diagnostic tool in detecting characteristics of OSSN before surgical resection. Although in vivo confocal microscopy cannot replace excisional biopsy for definitive diagnosis, it can be valuable for initial diagnosis and management of patients with OSSN.
Figures


References
-
- Lee GA, Hirst LW. Ocular surface squamous neoplasia. Surv Ophthalmol. 1995;39:429–450. - PubMed
-
- Finger PT, Tran H, Turbin RE, Perry HD, Abramson DH, Chin K. High-frequency ultra sonographic evaluation of conjunctival intra-epithelial neoplasia and squamous cell carcinoma. Arch Ophthalmol. 2003;121:168–172. - PubMed
-
- Tulvatana W, Tirakunwichcha S. Multifocal squamous cell carcinoma of the conjunctiva with intra ocular penetration in a patient with AIDS. Cornea. 2006;25:745–747. - PubMed
-
- Shields CL, Manchandia A, Subbiah R, Eagle RC, Jr, Shields JA. Pigmented squamous cell carcinoma insitu of the conjunctiva in 5 cases. Ophthalmology. 2008;115:1673–1678. - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

