Intermittent hypoxia conditioning protects mitochondrial cytochrome c oxidase of rat cerebellum from ethanol withdrawal stress
- PMID: 22403345
- PMCID: PMC3365408
- DOI: 10.1152/japplphysiol.01428.2011
Intermittent hypoxia conditioning protects mitochondrial cytochrome c oxidase of rat cerebellum from ethanol withdrawal stress
Abstract
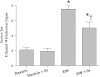
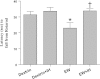
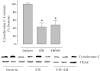
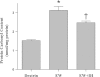
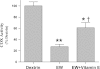
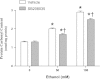
Intermittent hypoxia (IH) conditioning minimizes neurocognitive impairment and stabilizes brain mitochondrial integrity during ethanol withdrawal (EW) in rats, but the mitoprotective mechanism is unclear. We investigated whether IH conditioning protects a key mitochondrial enzyme, cytochrome c oxidase (COX), from EW stress by inhibiting mitochondrially directed apoptotic pathways involving cytochrome c, Bax, or phosphor-P38 (pP38). Male rats completed two cycles of a 4-wk ethanol diet (6.5%) and 3 wk of EW. An IH program consisting of 5-10 bouts of 5-8 min of mild hypoxia (9.5-10% inspired O(2)) and 4 min of reoxygenation for 20 consecutive days began 3 days before the first EW period. For some animals, vitamin E replaced IH conditioning to test the contributions of antioxidant mechanisms to IH's mitoprotection. During the second EW, cerebellar-related motor function was evaluated by measuring latency of fall from a rotating rod (Rotarod test). After the second EW, COX activity in cerebellar mitochondria was measured by spectrophotometry, and COX, cytochrome c, Bax, and pP38 content were analyzed by immunoblot. Mitochondrial protein oxidation was detected by measuring carbonyl contents and by immunochemistry. Earlier IH conditioning prevented motor impairment, COX inactivation, depletion of COX subunit 4, protein carbonylation, and P38 phosphorylation during EW. IH did not prevent cytochrome c depletion during EW, and Bax content was unaffected by EW ± IH. Vitamin E treatment recapitulated IH protection of COX, and P38 inhibition attenuated protein oxidation during EW. Thus IH protects COX and improves cerebellar function during EW by limiting P38-dependent oxidative damage.
Figures

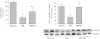
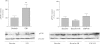
Similar articles
-
Intermittent hypoxia conditioning prevents behavioral deficit and brain oxidative stress in ethanol-withdrawn rats.J Appl Physiol (1985). 2008 Aug;105(2):510-7. doi: 10.1152/japplphysiol.90317.2008. Epub 2008 May 22. J Appl Physiol (1985). 2008. PMID: 18499779 Free PMC article.
-
Intermittent hypoxia training blunts cerebrocortical presenilin 1 overexpression and amyloid-β accumulation in ethanol-withdrawn rats.Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol. 2017 Jul 1;313(1):R10-R18. doi: 10.1152/ajpregu.00050.2017. Epub 2017 May 10. Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol. 2017. PMID: 28490448 Free PMC article.
-
Ethanol withdrawal acts as an age-specific stressor to activate cerebellar p38 kinase.Neurobiol Aging. 2011 Dec;32(12):2266-78. doi: 10.1016/j.neurobiolaging.2010.01.005. Epub 2010 Feb 1. Neurobiol Aging. 2011. PMID: 20122756 Free PMC article.
-
Alcohol withdrawal and brain injuries: beyond classical mechanisms.Molecules. 2010 Jul 20;15(7):4984-5011. doi: 10.3390/molecules15074984. Molecules. 2010. PMID: 20657404 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Alcohol Withdrawal and Cerebellar Mitochondria.Cerebellum. 2015 Aug;14(4):421-37. doi: 10.1007/s12311-014-0598-8. Cerebellum. 2015. PMID: 25195804 Review.
Cited by
-
Intermittent Hypoxia Training Prevents Deficient Learning-Memory Behavior in Mice Modeling Alzheimer's Disease: A Pilot Study.Front Aging Neurosci. 2021 Jul 1;13:674688. doi: 10.3389/fnagi.2021.674688. eCollection 2021. Front Aging Neurosci. 2021. PMID: 34276338 Free PMC article.
-
Bibliometric Analysis Study on the Mechanisms of Brain Energy Metabolism Disorders in Alzheimer's Disease From 2000 to 2020.Front Neurol. 2021 Jul 21;12:670220. doi: 10.3389/fneur.2021.670220. eCollection 2021. Front Neurol. 2021. PMID: 34354657 Free PMC article.
-
Hypoxic preconditioning alleviates ethanol neurotoxicity: the involvement of autophagy.Neurotox Res. 2013 Nov;24(4):472-7. doi: 10.1007/s12640-013-9390-7. Epub 2013 Apr 9. Neurotox Res. 2013. PMID: 23568540 Free PMC article.
-
Intermittent Hypoxic Conditioning Rescues Cognition and Mitochondrial Bioenergetic Profile in the Triple Transgenic Mouse Model of Alzheimer's Disease.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Jan 5;22(1):461. doi: 10.3390/ijms22010461. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 33466445 Free PMC article.
-
The Role of Presenilin-1 in the Excitotoxicity of Ethanol Withdrawal.J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2016 Sep;358(3):516-26. doi: 10.1124/jpet.116.233361. Epub 2016 Jun 8. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2016. PMID: 27278235 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Barca O, Costoya JA, Senaris RM, Arce VM. Interferon-beta protects astrocytes against tumour necrosis factor-induced apoptosis via activation of p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase. Exp Cell Res 314: 2231–2237, 2008 - PubMed
-
- Bishopric NH, Andreka P, Slepak T, Webster KA. Molecular mechanisms of apoptosis in the cardiac myocyte. Curr Opin Pharmacol 1: 141–150, 2001 - PubMed
-
- Bradford MM. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem 72: 248–254, 1976 - PubMed
-
- Cardoso SM, Proenca MT, Santos S, Santana I, Oliveira CR. Cytochrome c oxidase is decreased in Alzheimer's disease platelets. Neurobiol Aging 25: 105–110, 2004 - PubMed
-
- Chaparro-Huerta V, Flores-Soto ME, Gudino-Cabrera G, Rivera-Cervantes MC, Bitzer-Quintero OK, Beas-Zarate C. Role of p38 MAPK and pro-inflammatory cytokines expression in glutamate-induced neuronal death of neonatal rats. Int J Dev Neurosci 26: 487–495, 2008 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

