Antibacterial nanocomposite with calcium phosphate and quaternary ammonium
- PMID: 22403412
- PMCID: PMC3327730
- DOI: 10.1177/0022034512440579
Antibacterial nanocomposite with calcium phosphate and quaternary ammonium
Abstract
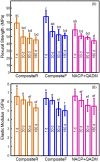
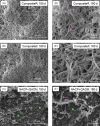
Secondary caries is a frequent reason for restoration failure, resulting from acidogenic bacteria and their biofilms. The objectives of this study were to: (1) develop a novel nanocomposite containing nanoparticles of amorphous calcium phosphate (NACP) and quaternary ammonium dimethacrylate (QADM); and (2) investigate its mechanical and antibacterial durability. A spray-drying technique yielded NACP with particle size of 116 nm. The nanocomposite contained NACP and reinforcement glass fillers, with QADM in the resin. Two commercial composites were tested as controls. Composites were inoculated with Streptococcus mutans. After 180-day water-aging, NACP+QADM nanocomposite had flexural strength and elastic modulus matching those of commercial controls (p > 0.1). NACP+QADM nanocomposite reduced the biofilm colony-forming units (CFU) by 3-fold, compared with commercial composites (p < 0.05). Metabolic activity and lactic acid production of biofilms on NACP+QADM were much less than those on commercial composites (p < 0.05). The antibacterial properties of NACP+QADM were maintained after water-aging for 30, 90, and 180 d (p > 0.05). In conclusion, the novel NACP-QADM nanocomposite greatly decreased biofilm metabolic activity, CFU, and lactic acid, while matching the load-bearing capability of commercial composites without antibacterial properties. The NACP-QADM nanocomposite with strong and durable antibacterial properties, together with its previously reported Ca-PO(4) release capability, may render it useful for caries-inhibiting restorations.
Conflict of interest statement
The author(s) declare no potential conflicts of interest with respect to the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article.
Figures


References
-
- Bayne SC, Thompson JY, Swift EJ, Jr, Stamatiades P, Wilkerson M. (1998). A characterization of first-generation flowable composites. J Am Dent Assoc 129:567-577 - PubMed
-
- Beyth N, Yudovin-Farber I, Bahir R, Domb AJ, Weiss EI. (2006). Antibacterial activity of dental composites containing quaternary ammonium polyethylenimine nanoparticles against Streptococcus mutans. Biomaterials 27:3995-4002 - PubMed
-
- Beyth N, Domb AJ, Weiss EI. (2007). An in vitro quantitative antibacterial analysis of amalgam and composite resins. J Dent 35:201-206 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

