Nanomedicine: towards development of patient-friendly drug-delivery systems for oncological applications
- PMID: 22403487
- PMCID: PMC3292417
- DOI: 10.2147/IJN.S25182
Nanomedicine: towards development of patient-friendly drug-delivery systems for oncological applications
Abstract
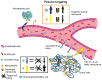
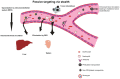
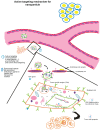
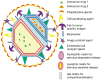
The focus on nanotechnology in cancer treatment and diagnosis has intensified due to the serious side effects caused by anticancer agents as a result of their cytotoxic actions on normal cells. This nonspecific action of chemotherapy has awakened a need for formulations capable of definitive targeting with enhanced tumor-killing. Nanooncology, the application of nanobiotechnology to the management of cancer, is currently the most important area of nanomedicine. Currently several nanomaterial-based drug-delivery systems are in vogue and several others are in various stages of development. Tumor-targeted drug-delivery systems are envisioned as magic bullets for cancer therapy and several groups are working globally for development of robust systems.
Keywords: cancer; drug-delivery systems; nanomedicine; patient-friendly.
Figures

References
-
- Zamboni WC. Concept and clinical evaluation of carrier-mediated anticancer agents. Oncologist. 2008;13:248–260. - PubMed
-
- Hanahan D, Weinberg RA. The hallmarks of cancer. Cell. 2000;100:57–70. - PubMed
-
- Byrne JD, Betancourt T, Brannon-Peppas L. Active targeting schemes for nanoparticle systems in cancer therapeutics. Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 2008;60:1615–1626. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

