Degradable gene delivery systems based on Pluronics-modified low-molecular-weight polyethylenimine: preparation, characterization, intracellular trafficking, and cellular distribution
- PMID: 22403492
- PMCID: PMC3292422
- DOI: 10.2147/IJN.S27117
Degradable gene delivery systems based on Pluronics-modified low-molecular-weight polyethylenimine: preparation, characterization, intracellular trafficking, and cellular distribution
Abstract
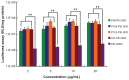
Background: Cationic copolymers consisting of polycations linked to nonionic amphiphilic block polymers have been evaluated as nonviral gene delivery systems, and a large number of different polymers and copolymers of linear, branched, and dendrimeric architectures have been tested in terms of their suitability and efficacy for in vitro and in vivo transfection. However, the discovery of new potent materials still largely relies on empiric approaches rather than a rational design. The authors investigated the relationship between the polymers' structures and their biological performance, including DNA compaction, toxicity, transfection efficiency, and the effect of cellular uptake.
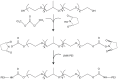
Methods: This article reports the synthesis and characterization of a series of cationic copolymers obtained by grafting polyethyleneimine with nonionic amphiphilic surfactant polyether-Pluronic(®) consisting of hydrophilic ethylene oxide and hydrophobic propylene oxide blocks. Transgene expression, cytotoxicity, localization of plasmids, and cellular uptake of these copolymers were evaluated following in vitro transfection of HeLa cell lines with various individual components of the copolymers.
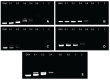
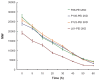
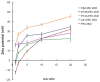
Results: Pluronics can exhibit biological activity including effects on enhancing DNA cellular uptake, nuclear translocation, and gene expression. The Pluronics with a higher hydrophilic-lipophilic balance value lead to homogeneous distribution in the cytoplasm; those with a lower hydrophilic-lipophilic balance value prefer to localize in the nucleus.
Conclusion: This Pluronic-polyethyleneimine system may be worth exploring as components in the cationic copolymers as the DNA or small interfering RNA/microRNA delivery system in the near future.
Keywords: Pluronics; cellular uptake; gene transfer; nonviral vectors; transfection efficiency.
Figures





Similar articles
-
Effect of Pluronic-block copolymers on the reduction of serum-mediated inhibition of gene transfer of polyethyleneimine-DNA complexes.Biotechnol Appl Biochem. 2003 Jun;37(Pt 3):267-71. doi: 10.1042/BA20020123. Biotechnol Appl Biochem. 2003. PMID: 12597775
-
Poly(ester amine) constructed from polyethylenimine and pluronic for gene delivery in vitro and in vivo.Drug Deliv. 2016 Nov;23(9):3224-3233. doi: 10.3109/10717544.2016.1162877. Epub 2016 Mar 29. Drug Deliv. 2016. PMID: 26960992
-
Design and formulation of polyplexes based on pluronic-polyethyleneimine conjugates for gene transfer.Bioconjug Chem. 2002 Sep-Oct;13(5):937-44. doi: 10.1021/bc025504w. Bioconjug Chem. 2002. PMID: 12236774
-
Block and graft copolymers and NanoGel copolymer networks for DNA delivery into cell.J Drug Target. 2000;8(2):91-105. doi: 10.3109/10611860008996855. J Drug Target. 2000. PMID: 10852341 Review.
-
Polymeric Drug Delivery System Based on Pluronics for Cancer Treatment.Molecules. 2021 Jun 12;26(12):3610. doi: 10.3390/molecules26123610. Molecules. 2021. PMID: 34204668 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Vectors for inhaled gene therapy in lung cancer. Application for nano oncology and safety of bio nanotechnology.Int J Mol Sci. 2012;13(9):10828-10862. doi: 10.3390/ijms130910828. Epub 2012 Aug 29. Int J Mol Sci. 2012. PMID: 23109824 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Peptide-Mediated Tumor Targeting by a Degradable Nano Gene Delivery Vector Based on Pluronic-Modified Polyethylenimine.Nanoscale Res Lett. 2016 Dec;11(1):122. doi: 10.1186/s11671-016-1337-5. Epub 2016 Mar 1. Nanoscale Res Lett. 2016. PMID: 26932761 Free PMC article.
-
HPV Oncogene Manipulation Using Nonvirally Delivered CRISPR/Cas9 or Natronobacterium gregoryi Argonaute.Adv Sci (Weinh). 2018 May 18;5(7):1700540. doi: 10.1002/advs.201700540. eCollection 2018 Jul. Adv Sci (Weinh). 2018. PMID: 30027026 Free PMC article.
-
Low-Molecular Weight Polyethylenimine Modified with Pluronic 123 and RGD- or Chimeric RGD-NLS Peptide: Characteristics and Transfection Efficacy of Their Complexes with Plasmid DNA.Molecules. 2016 May 18;21(5):655. doi: 10.3390/molecules21050655. Molecules. 2016. PMID: 27213305 Free PMC article.
-
Positively Charged Dendron Micelles Display Negligible Cellular Interactions.ACS Macro Lett. 2013 Jan 15;2(1):77-81. doi: 10.1021/mz300533w. Epub 2012 Dec 31. ACS Macro Lett. 2013. PMID: 23355959 Free PMC article.
References
-
- De Smedt SC, Demeester J, Hennink WE. Cationic polymer based gene delivery systems. Pharm Res. 2000;17(2):113–126. - PubMed
-
- Cho KC, Choi SH, Park TG. Low molecular weight PEI conjugated pluronic copolymer: useful additive for enhancing gene transfection efficiency. Macromol Res. 2006;14(3):348–353.
-
- Lee K, Bae KH, Lee Y, Lee SH, Ahn CH, Park TG. Pluronic/polyethylenimine shell crosslinked nanocapsules with embedded magnetite nanocrystals for magnetically triggered delivery of siRNA. Macromol Biosci. 2010;10(3):239–245. - PubMed
-
- Gebhart CL, Kabanov AV. Evaluation of polyplexes as gene transfer agents. J Control Release. 2001;73(2–3):401–416. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

