Risk factors of cryptogenic hepatocellular carcinoma in patients with low body mass index or without metabolic syndrome
- PMID: 22403499
- PMCID: PMC3295988
- DOI: 10.3904/kjim.2012.27.1.47
Risk factors of cryptogenic hepatocellular carcinoma in patients with low body mass index or without metabolic syndrome
Abstract
Background/aims: Many patients are diagnosed with cryptogenic hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) without metabolic syndrome (MS). We investigated the risk factors for cryptogenic HCC in patients with a low body mass index (BMI) or without MS.
Methods: Thirty-six patients were diagnosed with cryptogenic HCC over a 10-year period at a tertiary research hospital. Data including BMI score and risk factors for MS were analyzed retrospectively. Patients with fewer than two risk factors for MS (n = 16) were compared with those with two or more risk factors (n = 20). Patients with high BMI (≥ 23 kg/m(2), n = 20) were also compared with those with lower BMI (n = 16).
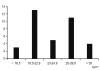
Results: Patients with fewer than two risk factors for MS were significantly more likely to smoke and be hepatitis B surface antibodies (anti-HBs)-positive vs. patients with two or more risk factors. However, only smoking was statistically significant on multivariate analysis. Peaks of BMI were observed in two regions. Lower BMI was significantly associated with the presence of anti-HBs compared with high BMI, although this association was not statistically significant on multivariate analysis.
Conclusions: Smoking is a potential risk factor for cryptogenic HCC in patients without MS. Remote hepatitis B virus infection may be a risk factor for cryptogenic HCC in patients without MS or with a low BMI.
Keywords: Carcinoma, hepatocellular; Hepatitis B antibodies; Metabolic syndrome; Smoking.
Conflict of interest statement
No potential conflict of interest relevant to this article was reported.
Figures
References
-
- Oh KC, Park SH, Park JC, et al. Is the prevalence of cryptogenic hepatocellular carcinoma increasing in Korea? Korean J Gastroenterol. 2005;45:45–51. - PubMed
-
- Bugianesi E, Leone N, Vanni E, et al. Expanding the natural history of nonalcoholic steatohepatitis: from cryptogenic cirrhosis to hepatocellular carcinoma. Gastroenterology. 2002;123:134–140. - PubMed
-
- Marrero JA, Fontana RJ, Su GL, Conjeevaram HS, Emick DM, Lok AS. NAFLD may be a common underlying liver disease in patients with hepatocellular carcinoma in the United States. Hepatology. 2002;36:1349–1354. - PubMed
-
- Starley BQ, Calcagno CJ, Harrison SA. Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease and hepatocellular carcinoma: a weighty connection. Hepatology. 2010;51:1820–1832. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical