A-Subclass ATP-Binding Cassette Proteins in Brain Lipid Homeostasis and Neurodegeneration
- PMID: 22403555
- PMCID: PMC3293240
- DOI: 10.3389/fpsyt.2012.00017
A-Subclass ATP-Binding Cassette Proteins in Brain Lipid Homeostasis and Neurodegeneration
Abstract
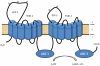
The A-subclass of ATP-binding cassette (ABC) transporters comprises 12 structurally related members of the evolutionarily highly conserved superfamily of ABC transporters. ABCA transporters represent a subgroup of "full-size" multispan transporters of which several members have been shown to mediate the transport of a variety of physiologic lipid compounds across membrane barriers. The importance of ABCA transporters in human disease is documented by the observations that so far four members of this protein family (ABCA1, ABCA3, ABCA4, ABCA12) have been causatively linked to monogenetic disorders including familial high-density lipoprotein deficiency, neonatal surfactant deficiency, degenerative retinopathies, and congenital keratinization disorders. Recent research also point to a significant contribution of several A-subfamily ABC transporters to neurodegenerative diseases, in particular Alzheimer's disease (AD). This review will give a summary of our current knowledge of the A-subclass of ABC transporters with a special focus on brain lipid homeostasis and their involvement in AD.
Keywords: ATP-binding cassette transporter; Alzheimer’s disease.
Figures
Similar articles
-
ABC A-subfamily transporters: structure, function and disease.Biochim Biophys Acta. 2006 May;1762(5):510-24. doi: 10.1016/j.bbadis.2006.01.011. Epub 2006 Feb 28. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2006. PMID: 16540294 Review.
-
Lipid transport by mammalian ABC proteins.Essays Biochem. 2011 Sep 7;50(1):265-90. doi: 10.1042/bse0500265. Essays Biochem. 2011. PMID: 21967062 Review.
-
ABC A-subclass proteins: gatekeepers of cellular phospho- and sphingolipid transport.Front Biosci. 2007 May 1;12:3177-93. doi: 10.2741/2305. Front Biosci. 2007. PMID: 17485292 Review.
-
The role of ATP-binding cassette subfamily A in the etiology of Alzheimer's disease.Mol Neurodegener. 2022 Apr 27;17(1):31. doi: 10.1186/s13024-022-00536-w. Mol Neurodegener. 2022. PMID: 35477481 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Role of ATP-binding cassette transporters in brain lipid transport and neurological disease.J Neurochem. 2008 Mar;104(5):1145-66. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.2007.05099.x. Epub 2007 Oct 31. J Neurochem. 2008. PMID: 17973979 Review.
Cited by
-
Differential phospholipid substrates and directional transport by ATP-binding cassette proteins ABCA1, ABCA7, and ABCA4 and disease-causing mutants.J Biol Chem. 2013 Nov 29;288(48):34414-26. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M113.508812. Epub 2013 Oct 4. J Biol Chem. 2013. PMID: 24097981 Free PMC article.
-
The ATP-Binding Cassette Transporter-2 (ABCA2) Overexpression Modulates Sphingosine Levels and Transcription of the Amyloid Precursor Protein (APP) Gene.Curr Alzheimer Res. 2015;12(9):847-59. doi: 10.2174/156720501209151019105834. Curr Alzheimer Res. 2015. PMID: 26510981 Free PMC article.
-
Autism Spectrum Disorder-Related Syndromes: Modeling with Drosophila and Rodents.Int J Mol Sci. 2019 Aug 21;20(17):4071. doi: 10.3390/ijms20174071. Int J Mol Sci. 2019. PMID: 31438473 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Cryo-EM structures of the ABCA4 importer reveal mechanisms underlying substrate binding and Stargardt disease.Nat Commun. 2021 Oct 8;12(1):5902. doi: 10.1038/s41467-021-26161-7. Nat Commun. 2021. PMID: 34625547 Free PMC article.
-
Leukocyte expression profiles reveal gene sets with prognostic value for seizure-free outcome following stereotactic laser amygdalohippocampotomy.Sci Rep. 2019 Jan 31;9(1):1086. doi: 10.1038/s41598-018-37763-5. Sci Rep. 2019. PMID: 30705324 Free PMC article.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

