Fos expression in neurons of the rat vestibulo-autonomic pathway activated by sinusoidal galvanic vestibular stimulation
- PMID: 22403566
- PMCID: PMC3289126
- DOI: 10.3389/fneur.2012.00004
Fos expression in neurons of the rat vestibulo-autonomic pathway activated by sinusoidal galvanic vestibular stimulation
Abstract
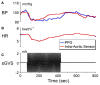
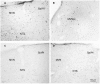
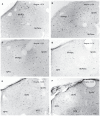
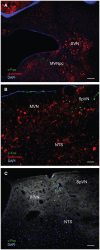
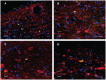
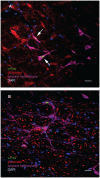
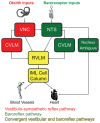
The vestibular system sends projections to brainstem autonomic nuclei that modulate heart rate and blood pressure in response to changes in head and body position with regard to gravity. Consistent with this, binaural sinusoidally modulated galvanic vestibular stimulation (sGVS) in humans causes vasoconstriction in the legs, while low frequency (0.02-0.04 Hz) sGVS causes a rapid drop in heart rate and blood pressure in anesthetized rats. We have hypothesized that these responses occur through activation of vestibulo-sympathetic pathways. In the present study, c-Fos protein expression was examined in neurons of the vestibular nuclei and rostral ventrolateral medullary region (RVLM) that were activated by low frequency sGVS. We found c-Fos-labeled neurons in the spinal, medial, and superior vestibular nuclei (SpVN, MVN, and SVN, respectively) and the parasolitary nucleus. The highest density of c-Fos-positive vestibular nuclear neurons was observed in MVN, where immunolabeled cells were present throughout the rostro-caudal extent of the nucleus. c-Fos expression was concentrated in the parvocellular region and largely absent from magnocellular MVN. c-Fos-labeled cells were scattered throughout caudal SpVN, and the immunostained neurons in SVN were restricted to a discrete wedge-shaped area immediately lateral to the IVth ventricle. Immunofluorescence localization of c-Fos and glutamate revealed that approximately one third of the c-Fos-labeled vestibular neurons showed intense glutamate-like immunofluorescence, far in excess of the stain reflecting the metabolic pool of cytoplasmic glutamate. In the RVLM, which receives a direct projection from the vestibular nuclei and sends efferents to preganglionic sympathetic neurons in the spinal cord, we observed an approximately threefold increase in c-Fos labeling in the sGVS-activated rats. We conclude that localization of c-Fos protein following sGVS is a reliable marker for sGVS-activated neurons of the vestibulo-sympathetic pathway.
Keywords: blood pressure; heart rate; orthostatic hypotension; otolith organs; rostral ventrolateral medulla; sympathetic nervous system; vasovagal syncope; vestibular nuclei.
Figures


References
-
- Armstrong D. M., Ross C. A., Pickel V. M., Joh T. H., Reis D. J. (1982). Distribution of dopamine-, noradrenaline-, and adrenaline-containing cell bodies in the rat medulla oblongata: Demonstration by the immunocytochemical localization of catecholamine biosynthetic enzymes. J. Comp. Neurol. 212, 173–187 10.1002/cne.902120207 - DOI - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

