Aloe vera induced biomimetic assemblage of nucleobase into nanosized particles
- PMID: 22403622
- PMCID: PMC3293877
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0032049
Aloe vera induced biomimetic assemblage of nucleobase into nanosized particles
Abstract
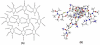
Aim: Biomimetic nano-assembly formation offers a convenient and bio friendly approach to fabricate complex structures from simple components with sub-nanometer precision. Recently, biomimetic (employing microorganism/plants) synthesis of metal and inorganic materials nano-particles has emerged as a simple and viable strategy. In the present study, we have extended biological synthesis of nano-particles to organic molecules, namely the anticancer agent 5-fluorouracil (5-FU), using Aloe vera leaf extract.
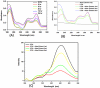
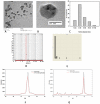
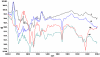
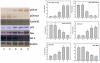
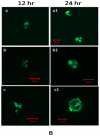
Methodology: The 5-FU nano- particles synthesized by using Aloe vera leaf extract were characterized by UV, FT-IR and fluorescence spectroscopic techniques. The size and shape of the synthesized nanoparticles were determined by TEM, while crystalline nature of 5-FU particles was established by X-ray diffraction study. The cytotoxic effects of 5-FU nanoparticles were assessed against HT-29 and Caco-2 (human adenocarcinoma colorectal) cell lines.
Results: Transmission electron microscopy and atomic force microscopic techniques confirmed nano-size of the synthesized particles. Importantly, the nano-assembled 5-FU retained its anticancer action against various cancerous cell lines.
Conclusion: In the present study, we have explored the potential of biomimetic synthesis of nanoparticles employing organic molecules with the hope that such developments will be helpful to introduce novel nano-particle formulations that will not only be more effective but would also be devoid of nano-particle associated putative toxicity constraints.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures

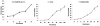
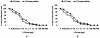
References
-
- Roco MC. Nanotechnology: convergence with modern biology and medicine. Curr Opin Biotechnol. 2003;14:337–343. - PubMed
-
- Gupta RB, Kompella Nanoparticle Technology for Drug Delivery. 2006. pp. 1–379. Taylor & Francis Group, New York, U.B. Eds.
-
- Wilkinson JM. Nanotechnology applications in medicine. Med Device Technol. 2003;14:29–31. - PubMed
-
- Schimidt J, Montemagno C. Using machines in cells Drug Discov. Today. 2002;7:500–503. - PubMed
-
- Lobenberg R, Kreuter J. Macrophage targeting of azidothymidine: a promising strategy for AIDS therapy. AIDS Res Hum Retroviruses. 1996;12:1709–1715. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

