Identifying low pH active and lactate-utilizing taxa within oral microbiome communities from healthy children using stable isotope probing techniques
- PMID: 22403637
- PMCID: PMC3293899
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0032219
Identifying low pH active and lactate-utilizing taxa within oral microbiome communities from healthy children using stable isotope probing techniques
Abstract
Background: Many human microbial infectious diseases including dental caries are polymicrobial in nature. How these complex multi-species communities evolve from a healthy to a diseased state is not well understood. Although many health- or disease-associated oral bacteria have been characterized in vitro, their physiology within the complex oral microbiome is difficult to determine with current approaches. In addition, about half of these species remain uncultivated to date with little known besides their 16S rRNA sequence. Lacking culture-based physiological analyses, the functional roles of uncultivated species will remain enigmatic despite their apparent disease correlation. To start addressing these knowledge gaps, we applied a combination of Magnetic Resonance Spectroscopy (MRS) with RNA and DNA based Stable Isotope Probing (SIP) to oral plaque communities from healthy children for in vitro temporal monitoring of metabolites and identification of metabolically active and inactive bacterial species.
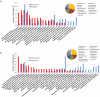
Methodology/principal findings: Supragingival plaque samples from caries-free children incubated with (13)C-substrates under imposed healthy (buffered, pH 7) and diseased states (pH 5.5 and pH 4.5) produced lactate as the dominant organic acid from glucose metabolism. Rapid lactate utilization upon glucose depletion was observed under pH 7 conditions. SIP analyses revealed a number of genera containing cultured and uncultivated taxa with metabolic capabilities at pH 5.5. The diversity of active species decreased significantly at pH 4.5 and was dominated by Lactobacillus and Propionibacterium species, both of which have been previously found within carious lesions from children.
Conclusions/significance: Our approach allowed for identification of species that metabolize carbohydrates under different pH conditions and supports the importance of Lactobacilli and Propionibacterium in the development of childhood caries. Identification of species within healthy subjects that are active at low pH can lead to a better understanding of oral caries onset and generate appropriate targets for preventative measures in the early stages.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
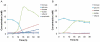




References
-
- Foster JS, Palmer RJ, Jr, Kolenbrander PE. Human oral cavity as a model for the study of genome-genome interactions. Biol Bull. 2003;204:200–204. - PubMed
-
- Kolenbrander PE, Jakubovics NS, Chalmers NI, Palmer RJ . Human Oral Multi-Species Biofilms: bacterial Communities in Health and Disease. In: Staffan Kjelleberg KG, Givskov Michael, Staffan Kjelleberg MG, editors. The Biofilm Mode of Life: Mechanisms and Adaptations. Norwich, UK: Horizon Scientific Press; 2007. pp. 175–194.
-
- Kolenbrander PE. Oral microbial communities: biofilms, interactions, and genetic systems. Annu Rev Microbiol. 2000;54:413–437. - PubMed
-
- Marsh PD, Bradshaw DJ. Dental plaque as a biofilm. J Ind Microbiol. 1995;15:169–175. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

