ATP utilization and RNA conformational rearrangement by DEAD-box proteins
- PMID: 22404686
- PMCID: PMC7761782
- DOI: 10.1146/annurev-biophys-050511-102243
ATP utilization and RNA conformational rearrangement by DEAD-box proteins
Abstract
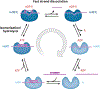
RNA helicase enzymes catalyze the in vivo folding and conformational re-arrangement of RNA. DEAD-box proteins (DBPs) make up the largest family of RNA helicases and are found across all phyla. DBPs are molecular motor proteins that utilize chemical energy in cycles of ATP binding, hydrolysis, and product release to perform mechanical work resulting in reorganization of cellular RNAs. DBPs contain a highly conserved motor domain helicase core. Auxiliary domains, enzymatic adaptations, and regulatory partner proteins contribute to the diversity of DBP function throughout RNA metabolism. In this review we focus on the current understanding of the DBP ATP utilization mechanism in rearranging and unwinding RNA structures. We discuss DBP structural properties, kinetic pathways, and thermodynamic features of nucleotide-dependent interactions with RNA. We highlight recent advances in the DBP field derived from biochemical and molecular biophysical investigations aimed at developing a quantitative mechanistic understanding of DBP molecular motor function.
Figures

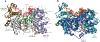

References
-
- Abdelhaleem M 2004. Do human RNA helicases have a role in cancer? Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1704:37–46 - PubMed
-
- Abramson R, Dever T, Lawson T, Ray B, Thach R, et al. 1987. The ATP-dependent interaction of eukaryotic initiation factors with mRNA. J. Biol. Chem 262:3826–32 - PubMed
-
- Akao Y 2009. A role of DEAD-box RNA helicase rck/p54 in cancer cells. Curr. Drug Ther 4:29–37
-
- Akao Y, Matsumoto K, Ohguchi K, Nakagawa Y, Yoshida H. 2006. Human DEAD-box/RNA unwindase rck/p54 contributes to maintenance of cell growth by affecting cell cycle in cultured cells. Int. J. Oncol 29:41–48 - PubMed
-
- Alcazar-Roman AR, Tran EJ, Guo S, Wente SR. 2006. Inositol hexakisphosphate and Gle1 activate the DEAD-box protein Dbp5 for nuclear mRNA export. Nat. Cell Biol 8:711–16 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

