Aging brain microenvironment decreases hippocampal neurogenesis through Wnt-mediated survivin signaling
- PMID: 22404871
- PMCID: PMC3350615
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1474-9726.2012.00816.x
Aging brain microenvironment decreases hippocampal neurogenesis through Wnt-mediated survivin signaling
Abstract
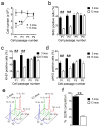
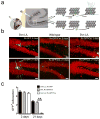
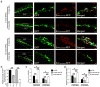
Accumulating evidence suggests that adult hippocampal neurogenesis relies on the controlled and continued proliferation of neural progenitor cells (NPCs). With age, neurogenesis decreases through mechanisms that remain unclear but are believed to involve changes in the NPC microenvironment. Here, we provide evidence that NPC proliferation in the adult brain is in part regulated by astrocytes via Wnt signaling and that this cellular cross-talk is modified in the aging brain, leading to decreased proliferation of NPCs. Furthermore, we show that astrocytes regulate the NPC cell cycle by acting on the expression levels of survivin, a known mitotic regulator. Among cell cycle genes found down-regulated in aged NPCs, survivin was the only one that restored NPC proliferation in the aged brain. Our results provide a mechanism for the gradual loss of neurogenesis in the brain associated with aging and suggest that targeted modulation of survivin expression directly or through Wnt signaling could be used to stimulate adult neurogenesis.
© 2012 The Authors. Aging Cell © 2012 Blackwell Publishing Ltd/Anatomical Society of Great Britain and Ireland.
Figures



References
-
- Alvarez-Buylla A, Temple S. Stem cells in the developing and adult nervous system. J Neurobiol. 1998;36:105–110. - PubMed
-
- Caldas H, Jiang Y, Holloway MP, Fangusaro J, Mahotka C, Conway EM, Altura RA. Survivin splice variants regulate the balance between proliferation and cell death. Oncogene. 2005;24:1994–2007. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

