Viral E3 ubiquitin ligase-mediated degradation of a cellular E3: viral mimicry of a cellular phosphorylation mark targets the RNF8 FHA domain
- PMID: 22405594
- PMCID: PMC3648639
- DOI: 10.1016/j.molcel.2012.02.004
Viral E3 ubiquitin ligase-mediated degradation of a cellular E3: viral mimicry of a cellular phosphorylation mark targets the RNF8 FHA domain
Abstract
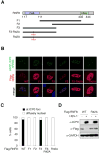
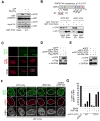
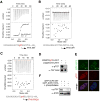
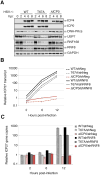
Viral hijacking of cellular processes relies on the ability to mimic the structure or function of cellular proteins. Many viruses encode ubiquitin ligases to facilitate infection, although the mechanisms by which they select their substrates are often unknown. The Herpes Simplex Virus type-1-encoded E3 ubiquitin ligase, ICP0, promotes infection through degradation of cellular proteins, including the DNA damage response E3 ligases RNF8 and RNF168. Here we describe a mechanism by which this viral E3 hijacks a cellular phosphorylation-based targeting strategy to degrade RNF8. By mimicking a cellular phosphosite, ICP0 binds RNF8 via the RNF8 forkhead associated (FHA) domain. Phosphorylation of ICP0 T67 by CK1 recruits RNF8 for degradation and thereby promotes viral transcription, replication, and progeny production. We demonstrate that this mechanism may constitute a broader viral strategy to target other cellular factors, highlighting the importance of this region of the ICP0 protein in countering intrinsic antiviral defenses.
Copyright © 2012 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures



References
-
- Bakkenist CJ, Kastan MB. DNA damage activates ATM through intermolecular autophosphorylation and dimer dissociation. Nature. 2003;421:499–506. - PubMed
-
- Burma S, Chen BP, Murphy M, Kurimasa A, Chen DJ. ATM phosphorylates histone H2AX in response to DNA double-strand breaks. J Biol Chem. 2001;276:42462–42467. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- R01 CA080100/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- CA14195/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- HHMI/Howard Hughes Medical Institute/United States
- R01 CA097093/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- P41 RR011823/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- R01 GM069530/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- CA80100/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- P30 CA021765/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- MC_UP_A550_1030/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- R01GM069530/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- MC_UU_12014/5/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- T32 CA009523/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- 5P30CA021765/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AI051686/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- AI067952/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- AI051686/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AI067952/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- CA097093/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- P30 CA014195/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

