Zinc fingers and homeoboxes 2 inhibits hepatocellular carcinoma cell proliferation and represses expression of Cyclins A and E
- PMID: 22406477
- PMCID: PMC3367107
- DOI: 10.1053/j.gastro.2012.02.049
Zinc fingers and homeoboxes 2 inhibits hepatocellular carcinoma cell proliferation and represses expression of Cyclins A and E
Abstract
Background & aims: Zinc-fingers and homeoboxes 2 (ZHX2) represses transcription of several genes associated with liver cancer. However, little is known about the role of ZHX2 in the development of hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC). We investigated the mechanisms by which ZHX2 might affect proliferation of HCC cells.
Methods: We overexpressed and knocked down ZHX2 in HCC cells and analyzed the effects on proliferation, colony formation, and the cell cycle. We also analyzed the effects of ZHX2 overexpression in growth of HepG2.2.15 tumor xenografts in nude mice. Chromatin immunoprecipitation and luciferase reporter assays were used to measure binding of ZHX2 target promoters. Levels of ZHX2 in HCC samples were evaluated by immunohistochemistry.
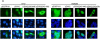
Results: ZHX2 overexpression significantly reduced proliferation of HCC cells and growth of tumor xenografts in mice; it led to G1 arrest and reduced levels of Cyclins A and E in HCC cell lines. ZHX2 bound to promoter regions of CCNA2 (which encodes Cyclin A) and CCNE1 (which encodes Cyclin E) and inhibited their transcription. Knockdown of Cyclin A or Cyclin E reduced the increased proliferation mediated by ZHX2 knockdown. Nuclear localization of ZHX2 was required for it to inhibit proliferation of HCC cells in culture and in mice. Nuclear localization of ZHX2 was reduced in human HCC samples, even in small tumors (diameter, <5 cm), compared with adjacent nontumor tissues. Moreover, reduced nuclear levels of ZHX2 correlated with reduced survival times of patients, high levels of tumor microvascularization, and hepatocyte proliferation.
Conclusions: ZHX2 inhibits HCC cell proliferation by preventing expression of Cyclins A and E, and reduces growth of xenograft tumors in mice. Loss of nuclear ZHX2 might be an early step in the development of HCC.
Copyright © 2012 AGA Institute. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures






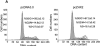
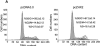
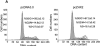
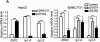
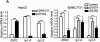
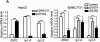
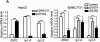
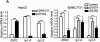
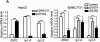











References
-
- Bosch FX, Ribes J, Diaz M, et al. Primary liver cancer: worldwide incidence and trends. Gastroenterology. 2004;127:S5–S16. - PubMed
-
- El-Serag HB, Mason AC. Risk factors for the rising rates of primary liver cancer in the United States. Arch Intern Med. 2000;160:3227–30. - PubMed
-
- Dragani TA. Risk of HCC: genetic heterogeneity and complex genetics. J Hepatol. 2010;52:252–7. - PubMed
-
- Abelev GI. Alpha-fetoprotein in ontogenesis and its association with malignant tumors. Adv Cancer Res. 1971;14:295–358. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

