EBNA3B-deficient EBV promotes B cell lymphomagenesis in humanized mice and is found in human tumors
- PMID: 22406538
- PMCID: PMC3314448
- DOI: 10.1172/JCI58092
EBNA3B-deficient EBV promotes B cell lymphomagenesis in humanized mice and is found in human tumors
Abstract
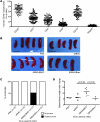
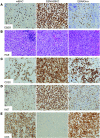
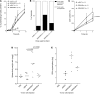
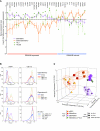
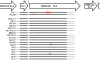
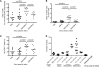
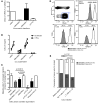
Epstein-Barr virus (EBV) persistently infects more than 90% of the human population and is etiologically linked to several B cell malignancies, including Burkitt lymphoma (BL), Hodgkin lymphoma (HL), and diffuse large B cell lymphoma (DLBCL). Despite its growth transforming properties, most immune-competent individuals control EBV infection throughout their lives. EBV encodes various oncogenes, and of the 6 latency-associated EBV-encoded nuclear antigens, only EBNA3B is completely dispensable for B cell transformation in vitro. Here, we report that infection with EBV lacking EBNA3B leads to aggressive, immune-evading monomorphic DLBCL-like tumors in NOD/SCID/γc-/- mice with reconstituted human immune system components. Infection with EBNA3B-knockout EBV (EBNA3BKO) induced expansion of EBV-specific T cells that failed to infiltrate the tumors. EBNA3BKO-infected B cells expanded more rapidly and secreted less T cell-chemoattractant CXCL10, reducing T cell recruitment in vitro and T cell-mediated killing in vivo. B cell lines from 2 EBV-positive human lymphomas encoding truncated EBNA3B exhibited gene expression profiles and phenotypic characteristics similar to those of tumor-derived lines from the humanized mice, including reduced CXCL10 secretion. Screening EBV-positive DLBCL, HL, and BL human samples identified additional EBNA3B mutations. Thus, EBNA3B is a virus-encoded tumor suppressor whose inactivation promotes immune evasion and virus-driven lymphomagenesis.
Figures
References
-
- Küppers R. B cells under influence: transformation of B cells by Epstein-Barr virus. Nat Rev Immunol. 2003;3(10):801–812. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

