Tumor angiogenesis mediated by myeloid cells is negatively regulated by CEACAM1
- PMID: 22406619
- PMCID: PMC3765079
- DOI: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-11-3016
Tumor angiogenesis mediated by myeloid cells is negatively regulated by CEACAM1
Erratum in
-
Correction: Tumor Angiogenesis Mediated by Myeloid Cells Is Negatively Regulated by CEACAM1.Cancer Res. 2016 Feb 15;76(4):984-5. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-15-3508. Cancer Res. 2016. PMID: 26880810 No abstract available.
Abstract
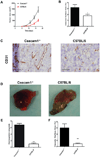
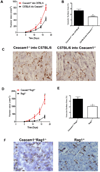
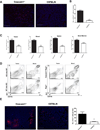
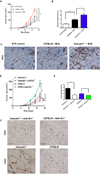
Bv8 (prokineticin 2) expressed by Gr1(+)CD11b(+) myeloid cells is critical for VEGF-independent tumor angiogenesis. Although granulocyte colony-stimulating factor (G-CSF) has been shown to be a key inducer of Bv8 expression, the basis for Bv8 production in driving tumor angiogenesis is undefined. Because the cell adhesion molecule CEACAM1, which is highly expressed on Gr1(+)CD11b(+) myeloid cells, is known to regulate G-CSF receptor (G-CSFR) signaling, we hypothesized that CEACAM1 would regulate Bv8 production in these cells. In support of this hypothesis, we found that Bv8 expression was elevated in Gr1(+)CD11b(+) cells from Ceacam1-deficient mice implanted with B16 melanoma, increasing the infiltration of Gr1(+)CD11b(+) myeloid cells in melanoma tumors and enhancing their growth and angiogenesis. Furthermore, treatment with anti-Gr1 or anti-Bv8 or anti-G-CSF monoclonal antibody reduced myeloid cell infiltration, tumor growth, and angiogenesis to levels observed in tumor-bearing wild-type (WT) mice. Reconstitution of CEACAM1-deficient mice with WT bone marrow cells restored tumor infiltration of Gr1(+)CD11b(+) cells along with tumor growth and angiogenesis to WT levels. Treatment of tumor-bearing WT mice with anti-CEACAM1 antibody limited tumor outgrowth and angiogenesis, albeit to a lesser extent. Tumor growth in Ceacam1-deficient mice was not affected significantly in Rag(-/-) background, indicating that CEACAM1 expression in T and B lymphocytes had a negligible role in this pathway. Together, our findings show that CEACAM1 negatively regulates Gr1(+)CD11b(+) myeloid cell-dependent tumor angiogenesis by inhibiting the G-CSF-Bv8 signaling pathway.
©2012 AACR
Conflict of interest statement
There are no conflicts of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Bv8 regulates myeloid-cell-dependent tumour angiogenesis.Nature. 2007 Dec 6;450(7171):825-31. doi: 10.1038/nature06348. Nature. 2007. PMID: 18064003
-
Induction of Bv8 expression by granulocyte colony-stimulating factor in CD11b+Gr1+ cells: key role of Stat3 signaling.J Biol Chem. 2012 Jun 1;287(23):19574-84. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M111.326801. Epub 2012 Apr 23. J Biol Chem. 2012. PMID: 22528488 Free PMC article.
-
Refractoriness to antivascular endothelial growth factor treatment: role of myeloid cells.Cancer Res. 2008 Jul 15;68(14):5501-4. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-08-0925. Cancer Res. 2008. PMID: 18632597 Review.
-
G-CSF-initiated myeloid cell mobilization and angiogenesis mediate tumor refractoriness to anti-VEGF therapy in mouse models.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2009 Apr 21;106(16):6742-7. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0902280106. Epub 2009 Apr 3. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2009. PMID: 19346489 Free PMC article.
-
Role of myeloid cells in vascular endothelial growth factor-independent tumor angiogenesis.Curr Opin Hematol. 2010 May;17(3):219-24. doi: 10.1097/MOH.0b013e3283386660. Curr Opin Hematol. 2010. PMID: 20308892 Review.
Cited by
-
Stromal CEACAM1 expression regulates colorectal cancer metastasis.Oncoimmunology. 2012 Oct 1;1(7):1205-1207. doi: 10.4161/onci.20735. Oncoimmunology. 2012. PMID: 23170281 Free PMC article.
-
CEACAM1 as a multi-purpose target for cancer immunotherapy.Oncoimmunology. 2017 May 16;6(7):e1328336. doi: 10.1080/2162402X.2017.1328336. eCollection 2017. Oncoimmunology. 2017. PMID: 28811966 Free PMC article. Review.
-
miRNA-342 Regulates CEACAM1-induced Lumen Formation in a Three-dimensional Model of Mammary Gland Morphogenesis.J Biol Chem. 2016 Aug 5;291(32):16777-86. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M115.710152. Epub 2016 Jun 14. J Biol Chem. 2016. PMID: 27302063 Free PMC article.
-
Bone marrow derived myeloid cells orchestrate antiangiogenic resistance in glioblastoma through coordinated molecular networks.Cancer Lett. 2015 Dec 28;369(2):416-26. doi: 10.1016/j.canlet.2015.09.004. Epub 2015 Sep 21. Cancer Lett. 2015. PMID: 26404753 Free PMC article.
-
Chimeric Mouse model to track the migration of bone marrow derived cells in glioblastoma following anti-angiogenic treatments.Cancer Biol Ther. 2016;17(3):280-90. doi: 10.1080/15384047.2016.1139243. Epub 2016 Jan 21. Cancer Biol Ther. 2016. PMID: 26797476 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Shojaei F, Ferrara N. Refractoriness to antivascular endothelial growth factor treatment: role of myeloid cells. Cancer Res. 2008;68:5501–5504. - PubMed
-
- Yang L, DeBusk LM, Fukuda K, Fingleton B, Green-Jarvis B, Shyr Y, et al. Expansion of myeloid immune suppressor Gr+CD11b+ cells in tumor-bearing host directly promotes tumor angiogenesis. Cancer Cell. 2004;6:409–421. - PubMed
-
- Shojaei F, Wu X, Malik AK, Zhong C, Baldwin ME, Schanz S, et al. Tumor refractoriness to anti-VEGF treatment is mediated by CD11b+Gr1+ myeloid cells. Nat Biotechnol. 2007;25:911–920. - PubMed
-
- Shojaei F, Wu X, Zhong C, Yu L, Liang XH, Yao J, et al. Bv8 regulates myeloid-cell-dependent tumour angiogenesis. Nature. 2007;450:825–831. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

