CC2D1A is a regulator of ESCRT-III CHMP4B
- PMID: 22406677
- PMCID: PMC3433253
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jmb.2012.02.044
CC2D1A is a regulator of ESCRT-III CHMP4B
Abstract
Endosomal sorting complexes required for transport (ESCRTs) regulate diverse processes ranging from receptor sorting at endosomes to distinct steps in cell division and budding of some enveloped viruses. Common to all processes is the membrane recruitment of ESCRT-III that leads to membrane fission. Here, we show that CC2D1A is a novel regulator of ESCRT-III CHMP4B function. We demonstrate that CHMP4B interacts directly with CC2D1A and CC2D1B with nanomolar affinity by forming a 1:1 complex. Deletion mapping revealed a minimal CC2D1A-CHMP4B binding construct, which includes a short linear sequence within the third DM14 domain of CC2D1A. The CC2D1A binding site on CHMP4B was mapped to the N-terminal helical hairpin. Based on a crystal structure of the CHMP4B helical hairpin, two surface patches were identified that interfere with CC2D1A interaction as determined by surface plasmon resonance. Introducing these mutations into a C-terminal truncation of CHMP4B that exerts a potent dominant negative effect on human immunodeficiency virus type 1 budding revealed that one of the mutants lost this effect completely. This suggests that the identified CC2D1A binding surface might be required for CHMP4B polymerization, which is consistent with the finding that CC2D1A binding to CHMP4B prevents CHMP4B polymerization in vitro. Thus, CC2D1A might act as a negative regulator of CHMP4B function.
Copyright © 2012. Published by Elsevier Ltd.
Figures

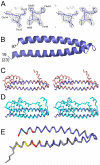

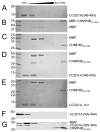

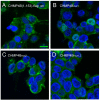

Similar articles
-
Structural Basis for Regulation of ESCRT-III Complexes by Lgd.Cell Rep. 2017 May 30;19(9):1750-1757. doi: 10.1016/j.celrep.2017.05.026. Cell Rep. 2017. PMID: 28564595 Free PMC article.
-
Regulation of CHMP4/ESCRT-III function in human immunodeficiency virus type 1 budding by CC2D1A.J Virol. 2012 Apr;86(7):3746-56. doi: 10.1128/JVI.06539-11. Epub 2012 Jan 18. J Virol. 2012. PMID: 22258254 Free PMC article.
-
CC2D1A and CC2D1B regulate degradation and signaling of EGFR and TLR4.Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2016 Nov 11;480(2):280-287. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2016.10.053. Epub 2016 Oct 18. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2016. PMID: 27769858
-
The regulation of Endosomal Sorting Complex Required for Transport and accessory proteins in multivesicular body sorting and enveloped viral budding - An overview.Int J Biol Macromol. 2019 Apr 15;127:1-11. doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2019.01.015. Epub 2019 Jan 4. Int J Biol Macromol. 2019. PMID: 30615963 Review.
-
ESCRT & Co.Biol Cell. 2010 Mar 12;102(5):293-318. doi: 10.1042/BC20090161. Biol Cell. 2010. PMID: 20222872 Review.
Cited by
-
Abscission is regulated by the ESCRT-III protein shrub in Drosophila germline stem cells.PLoS Genet. 2015 Feb 3;11(2):e1004653. doi: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1004653. eCollection 2015 Feb. PLoS Genet. 2015. PMID: 25647097 Free PMC article.
-
Structures, Functions, and Dynamics of ESCRT-III/Vps4 Membrane Remodeling and Fission Complexes.Annu Rev Cell Dev Biol. 2018 Oct 6;34:85-109. doi: 10.1146/annurev-cellbio-100616-060600. Epub 2018 Aug 10. Annu Rev Cell Dev Biol. 2018. PMID: 30095293 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Chicken CH25H inhibits ALV-J replication by promoting cellular autophagy.Front Immunol. 2023 Feb 15;14:1093289. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2023.1093289. eCollection 2023. Front Immunol. 2023. PMID: 36875122 Free PMC article.
-
Structural Basis for Regulation of ESCRT-III Complexes by Lgd.Cell Rep. 2017 May 30;19(9):1750-1757. doi: 10.1016/j.celrep.2017.05.026. Cell Rep. 2017. PMID: 28564595 Free PMC article.
-
Structural Analysis of the ESCRT-III Regulator Lethal(2) Giant Discs/Coiled-Coil and C2 Domain-Containing Protein 1 (Lgd/CC2D1).Cells. 2024 Jul 10;13(14):1174. doi: 10.3390/cells13141174. Cells. 2024. PMID: 39056756 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Matsuda A, Suzuki Y, Honda G, Muramatsu S, Matsuzaki O, Nagano Y, Doi T, Shimotohno K, Harada T, Nishida E, Hayashi H, Sugano S. Largescale identification and characterization of human genes that activate NF-kappaB and MAPK signaling pathways. Oncogene. 2003;22:3307–3318. - PubMed
-
- Rogaeva A, Albert PR. The mental retardation gene CC2D1A/Freud-1 encodes a long isoform that binds conserved DNA elements to repress gene transcription. Eur J Neurosci. 2007;26:965–74. - PubMed
-
- Szewczyk B, Albert PR, Rogaeva A, Fitzgibbon H, May WL, Rajkowska G, Miguel-Hidalgo JJ, Stockmeier CA, Woolverton WL, Kyle PB, Wang Z, Austin MC. Decreased expression of Freud-1/CC2D1A, a transcriptional repressor of the 5-HT(1A) receptor, in the prefrontal cortex of subjects with major depression. Int J Neuropsychopharmacol. 2011;13:1089–101. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Rogaeva A, Galaraga K, Albert PR. The Freud-1/CC2D1A family: transcriptional regulators implicated in mental retardation. J Neurosci Res. 2007;85:2833–8. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

