MicroRNA regulation of smooth muscle gene expression and phenotype
- PMID: 22406821
- PMCID: PMC5226630
- DOI: 10.1097/MOH.0b013e3283523e57
MicroRNA regulation of smooth muscle gene expression and phenotype
Abstract
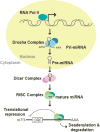
Purpose of review: In this review, we summarize the recent advances regarding microRNA (miRNA) functions in the regulation of vascular smooth muscle cell (VSMC) differentiation and phenotypic modulation.
Recent findings: Multiple miRNAs are found to be responsible for VSMC differentiation and proliferation under physiological or pathological condition. A single miRNA downregulates multiple targets, whereas a single gene is regulated by multiple miRNAs to modulate a specific aspect of VSMC phenotype.
Summary: The phenotype of VSMCs is dynamically regulated in response to environmental stimuli. Deregulation of phenotype switching is associated with vascular diseases. Several miRNAs have been found to be highly expressed in the vasculature, to modulate VSMC phenotype, and to be dysregulated in vascular diseases. By regulating mRNA and/or protein levels posttranscriptionally, miRNAs provide a delicate regulation in the complex molecular networks that regulate the vascular system. Understanding the functions of miRNAs in the regulation of VSMC differentiation and phenotype switching provides new insights into the mechanisms of vascular development, function, and dysfunction.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Micromanaging vascular smooth muscle cell differentiation and phenotypic modulation.Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2011 Nov;31(11):2370-7. doi: 10.1161/ATVBAHA.111.226670. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2011. PMID: 22011749 Free PMC article. Review.
-
How do microRNAs affect vascular smooth muscle cell biology?Curr Opin Lipidol. 2012 Oct;23(5):405-11. doi: 10.1097/MOL.0b013e32835719a1. Curr Opin Lipidol. 2012. PMID: 22964990 Review.
-
MicroRNA-31 controls phenotypic modulation of human vascular smooth muscle cells by regulating its target gene cellular repressor of E1A-stimulated genes.Exp Cell Res. 2013 May 1;319(8):1165-75. doi: 10.1016/j.yexcr.2013.03.010. Epub 2013 Mar 19. Exp Cell Res. 2013. PMID: 23518389
-
MicroRNA and vascular smooth muscle cells.Vitam Horm. 2011;87:321-39. doi: 10.1016/B978-0-12-386015-6.00034-2. Vitam Horm. 2011. PMID: 22127249 Review.
-
Smooth muscle cell-driven vascular diseases and molecular mechanisms of VSMC plasticity.Cell Signal. 2018 Dec;52:48-64. doi: 10.1016/j.cellsig.2018.08.019. Epub 2018 Aug 30. Cell Signal. 2018. PMID: 30172025 Review.
Cited by
-
Therapeutic Potential of Modulating microRNAs in Atherosclerotic Vascular Disease.Curr Vasc Pharmacol. 2013 May 13. Online ahead of print. Curr Vasc Pharmacol. 2013. PMID: 23713860 Free PMC article.
-
miR-137 and its target T-type CaV 3.1 channel modulate dedifferentiation and proliferation of cerebrovascular smooth muscle cells in simulated microgravity rats by regulating calcineurin/NFAT pathway.Cell Prolif. 2020 Mar;53(3):e12774. doi: 10.1111/cpr.12774. Epub 2020 Feb 8. Cell Prolif. 2020. PMID: 32034930 Free PMC article.
-
Toll-like Receptors in the Vascular System: Sensing the Dangers Within.Pharmacol Rev. 2016 Jan;68(1):142-67. doi: 10.1124/pr.114.010090. Pharmacol Rev. 2016. PMID: 26721702 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Targeting miRNA with flavonoids: unlocking novel pathways in cardiovascular disease management.Front Pharmacol. 2025 Mar 6;16:1532986. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2025.1532986. eCollection 2025. Front Pharmacol. 2025. PMID: 40115258 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Role of miRNAs in vascular development.Noncoding RNA Res. 2022 Sep 29;8(1):1-7. doi: 10.1016/j.ncrna.2022.09.010. eCollection 2023 Mar. Noncoding RNA Res. 2022. PMID: 36262425 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Owens GK, Kumar MS, Wamhoff BR. Molecular regulation of vascular smooth muscle cell differentiation in development and disease. Physiological Reviews. 2004;84:767–801. - PubMed
-
- Owens GK. Regulation of Differentiation of Vascular Smooth-Muscle Cells. Physiological Reviews. 1995;75:487–517. - PubMed
-
- Tallquist M, Kazlauskas A. PDGF signaling in cells and mice. Cytokine & Growth Factor Reviews. 2004;15:205–213. - PubMed
-
- ten Dijke P, Arthur HM. Extracellular control of TGF beta signalling in vascular development and disease. Nature Reviews Molecular Cell Biology. 2007;8:857–869. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

