A telomere-dependent DNA damage checkpoint induced by prolonged mitotic arrest
- PMID: 22407014
- PMCID: PMC3319806
- DOI: 10.1038/nsmb.2245
A telomere-dependent DNA damage checkpoint induced by prolonged mitotic arrest
Abstract
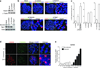
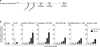
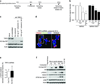
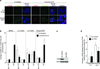
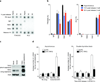
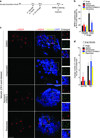
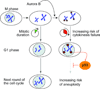
Telomere shortening and disruption of telomeric components are pathways that induce telomere deprotection. Here we describe another pathway, in which prolonged mitotic arrest induces damage signals at telomeres in human cells. Exposure to microtubule drugs, kinesin inhibitors, proteasome inhibitors or the disruption of proper chromosome cohesion resulted in the formation of damage foci at telomeres. Induction of mitotic telomere deprotection coincided with dissociation of TRF2 from telomeres, telomeric 3'-overhang degradation and ATM activation, and deprotection could be suppressed by TRF2 overexpression or inhibition of Aurora B kinase. Normal cells that escaped from prolonged mitotic arrest halted in the following G1 phase, whereas cells lacking p53 continued to cycle and became aneuploid. We propose a telomere-dependent mitotic-duration monitoring system that reacts to improper progression through mitosis.
Figures

References
-
- van Steensel B, Smogorzewska A, de Lange T. TRF2 protects human telomeres from end-to-end fusions. Cell. 1998;92:401–413. - PubMed
-
- Karlseder J, Broccoli D, Dai Y, Hardy S, de Lange T. p53- and ATM-dependent apoptosis induced by telomeres lacking TRF2. Science. 1999;283:1321–1325. - PubMed
-
- Denchi EL, de Lange T. Protection of telomeres through independent control of ATM and ATR by TRF2 and POT1. Nature. 2007;448:1068–1071. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

